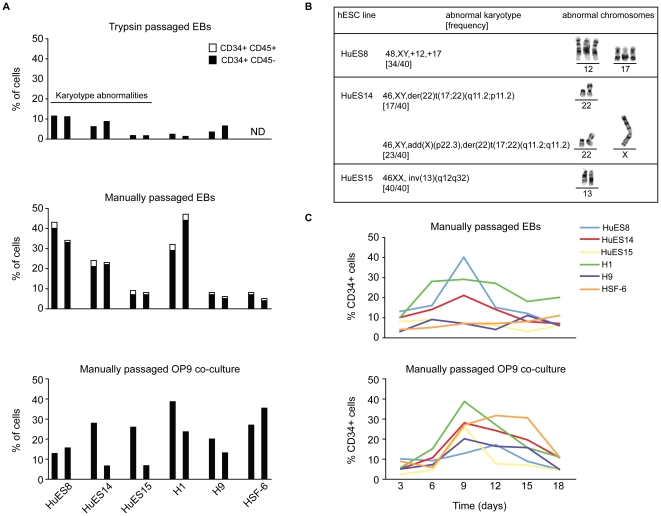
Figure 1. Comparative analysis of hemangioblast development from independently-derived hESC lines.
Several hESC lines were differentiated as embryoid bodies (EB) for nine days after several trypsin passages (A, top panel) or after several manual passages (A, middle panel) in EB media without lineage-skewing cytokines. CD34+ and CD34+CD45+ development was determined by flow cytometric analysis of several cell surface markers indicative of differentiation state. The proportion of hESC-derived CD34+CD45− cells is presented on differentiating hESCs in black. The proportion of CD34+CD45+ progenitors is indicated in white. HuES8, HuES14, and HuES15 cell lines were highly susceptible to gross karyotypic abnormalities during trypsin passage (as indicated). H1, H9, and HSF6 manually passaged cells had previously been passaged with trypsin (>5 manual passages before differentiation). (A, bottom panel) Independently-derived hESC were differentiated on an OP9 monolayer for nine days, and CD34 and CD45 cell surface expression analyzed by flow cytometry. Two representative experiments of each condition are presented. (B) Abnormal karyotypes observed in trypsin passaged cells. (C) Representative time course of CD34 expression on manually passaged, independently-derived hESCs differentiated as EBs or on an OP9 monolayer. CD34 expression was analyzed on days 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18.