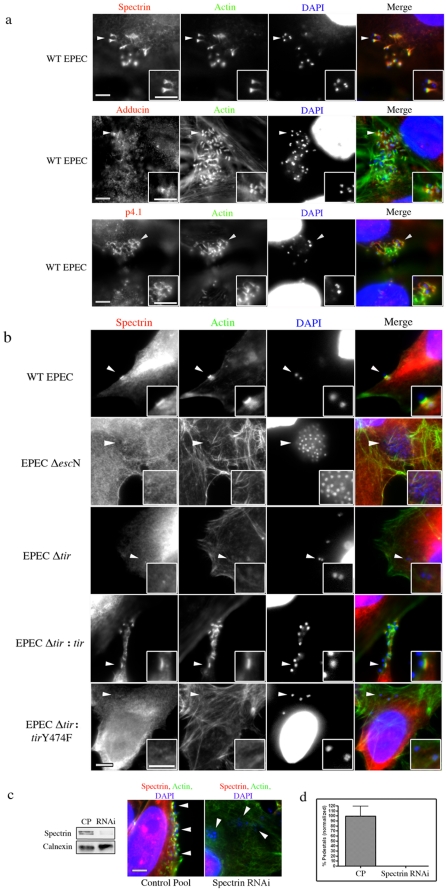
Figure 1. Characterizing the role of the spectrin cytoskeleton during EPEC infections.
(a) HeLa cells were infected with EPEC and immunolocalized with antibodies to spectrin, adducin and p4.1 together with probes to actin and DAPI. Arrowheads indicate areas of interest that are found in the insets. (b) Immunolocalization of spectrin to sites of wild-type (WT) EPEC attachment and to EPEC effector mutants: ΔescN, Δtir, Δtir:tir, Δtir:tirY474F. (c) Western blot of siRNA treated HeLa cells targeted against spectrin (Spectrin RNAi) and non-targeting control pool siRNA (CP). Calnexin was used as a loading control. Immunofluorescent image of spectrin RNAi, attached bacteria show they are unable to form pedestals. (d) Quantification of the number of bacteria forming pedestals. For each treatment, 3 independent experiments were run; for microscopy counts n = 3 for each experiment, error bars show s.e.m. Statistics were not run due to a complete absence of pedestals in infected RNAi samples Scale bars are 5 µm.