Figure 3.
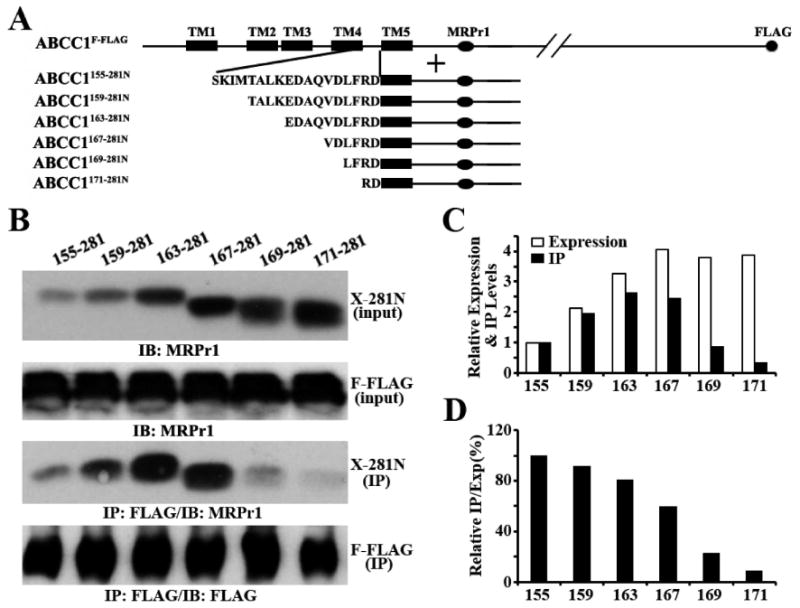
Role of ECL3 in dimerization. (A) Schematic diagram of ABCC1F-FLAG and the constructs containing ECL3 and TM5. TM5 and ECL3 are shown as a box and as a sequence of amino acids, respectively. The MRPr1 epitope and the FLAG tag are shown as an oval and circle, respectively. (B) Expression (input panels) and co-immunoprecipitation (IP panels) of the constructs containing ECL3 and TM5. The constructs containing ECL3 and TM5 were transiently transfected into HEK293 cells with stable expression of ABCC1F-FLAG followed by co-immunoprecipitation using the anti-FLAG antibody and Western blot analysis probed with the MRPr1 or FLAG antibody. (C and D) Quantification of expression and co-immunoprecipitation. The expression and co-immunoprecipitation levels of constructs containing ECL3 and TM5 in panel B were quantified using ScnImage and normalized to that of the shortest ABCC1155–281 construct (C) followed by calculation of the relative ratio of co-immunoprecipitation to expression level (D).
