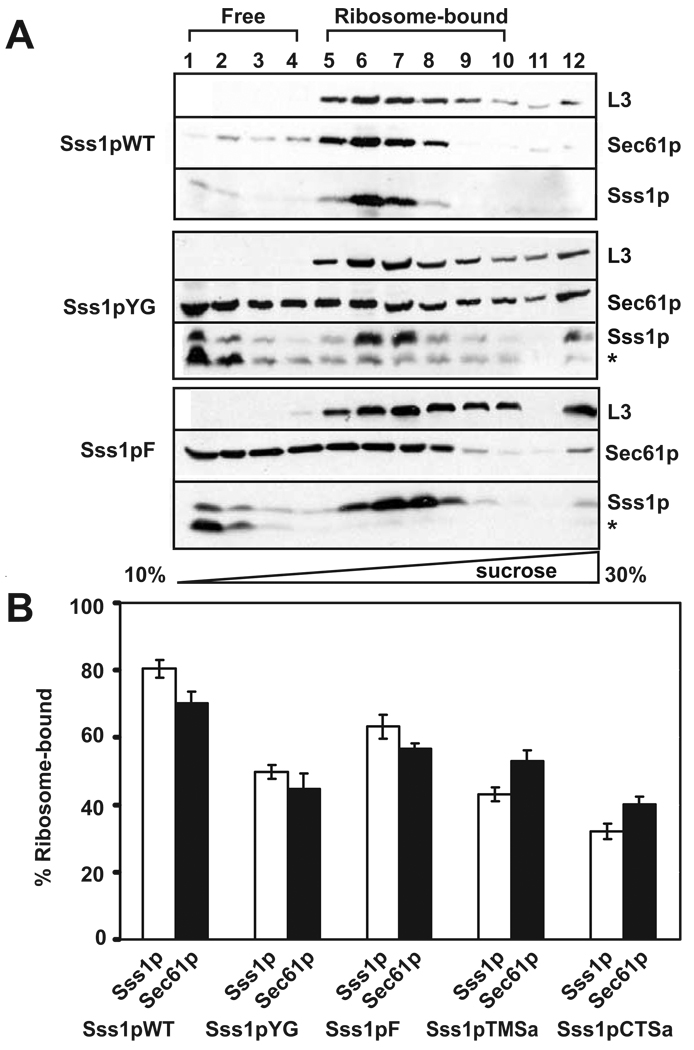
Figure 3. Sec61 complexes isolated from strains expressing mutant Sss1p proteins are defective for ribosome binding.
(A) Post-nuclear membranes isolated from yeast strains expressing wild-type Sss1p, Sss1pYG or Sss1pF were solubilized in a low ionic strength buffer to preserve the interaction with the ribosomes. Complexes resolved by sucrose gradient centrifugation in the same buffer containing a linear gradient of 10 to 30% sucrose were precipitated, separated by SDS-PAGE, and identified by immunoblotting with antibodies to the yeast 60S ribosomal protein L3, Sec61p and Sss1p. The sedimentation position of the ribosomes is indicated. * denotes a degradation product of Sss1p. (B) The amount of Sss1p (white bars) and Sec61p (black bars) that co-fractionated with the L3 peak fractions was quantified as a percent of the total (excluding fraction 13) for multiple experiments (described in (A)) for the indicated Sss1p mutants. Averages of 6 independent experiments are shown for all constructs except Sss1pYG (7) and Sss1pCTSa (5). All data are statistically significantly different from the wild type (p < 0.005)