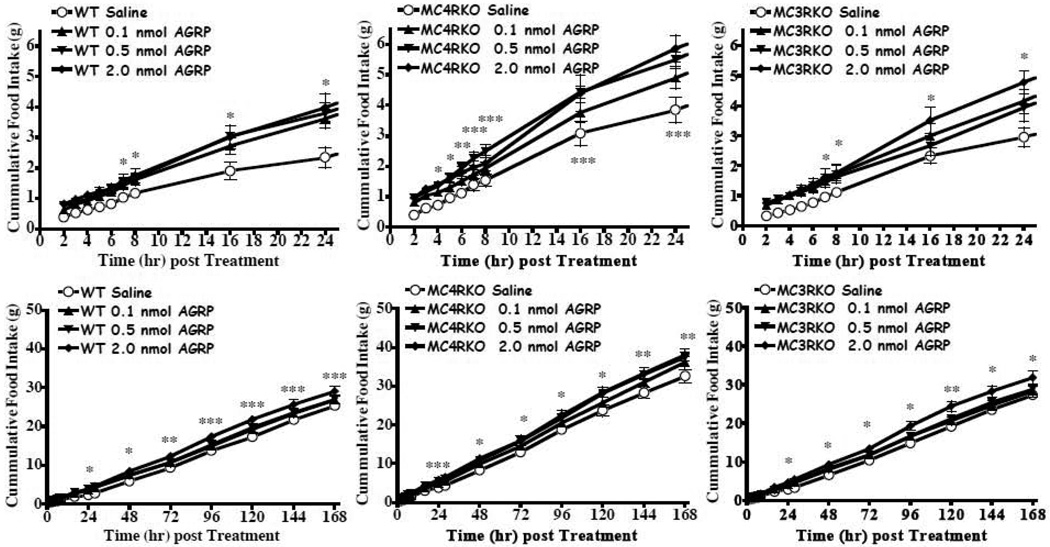
Figure 7.
Effect of AGRP(86-132) on food intake (mean ± S.E.M.) in satiated wild type, MC4KO, and MC3KO littermate mice. For all the mice, statistically increased food intake was observed relative to the saline control (p<0.0001, n=8–9 per group). A) In the wild type mice the 2.0 nmol dose statistically increased food intake relative to saline starting at t=7h and continued to remain statistically significant for the duration of the experiment (*p<0.05). B) In the MC4KO mice, the 0.5 and 2.0 nmol doses statistically increased food intake relative to saline starting at t=5h and t= 4h, respectively, and continued to remain statistically significant for the duration of the experiment (*p<0.05). C) B) In the MC3KO mice, the 2.0 nmol dose statistically increased food intake relative to saline starting at t=7h and continued to remain statistically significant for the duration of the experiment (*p<0.05). *p<0.05, ** p<0.01, ***p<0.001