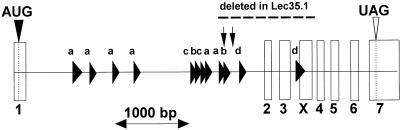
Figure 1.
Exon-intron organization of the hamster Lec35 gene. A fragment of normal CHO-K1 genomic DNA, ∼5 kbp, was amplified by LA-PCR (Takara Shuzo, Tokyo, Japan) with 5′ UTR and 3′ UTR primers from SL15. The fragment was gel-purified and used directly for automated DNA sequence analysis on both strands by using various sequencing primers suggested by SL15 cDNA sequence (GenBank accession U55387) as well as sequence obtained from introns. Exon-intron boundaries were deduced by directly comparing the genomic and cDNA sequences. Exon X was identified in a rare nonfunctional clone from the original cDNA library (Ware et al., 1996). Inclusion of exon X altered the 5′ splice junction of exon 4. Rodent genomic repetitive elements (Table 1; Jurka et al., 1996) are indicated by horizontal arrowheads: a, B1 class; b, B2 class; c, B3 class; d, RSINE1 class. Two BamHI sites identified by sequencing and used for restriction enzyme digests are noted by the downward vertical arrows. Translation initiation (AUG) and termination (UAG) sites are shown by vertical arrowheads. The entire annotated sequence has been deposited with GenBank (accession AF250376). A region extending from within intron 1 through exon X that appears deleted in the Lec35.1 allele (see text) is indicated. Because the Lec35.1 mutation is recessive, it is highly likely that the parental cell that gave rise to the Lec35.1 mutant had a single copy of a normal allele at the Lec35 locus. It is highly unlikely that the exact same deletion occurred twice in a single cell starting with two normal Lec35 alleles.