Figure 4. MEK Activation during Cell Cycle Progression.
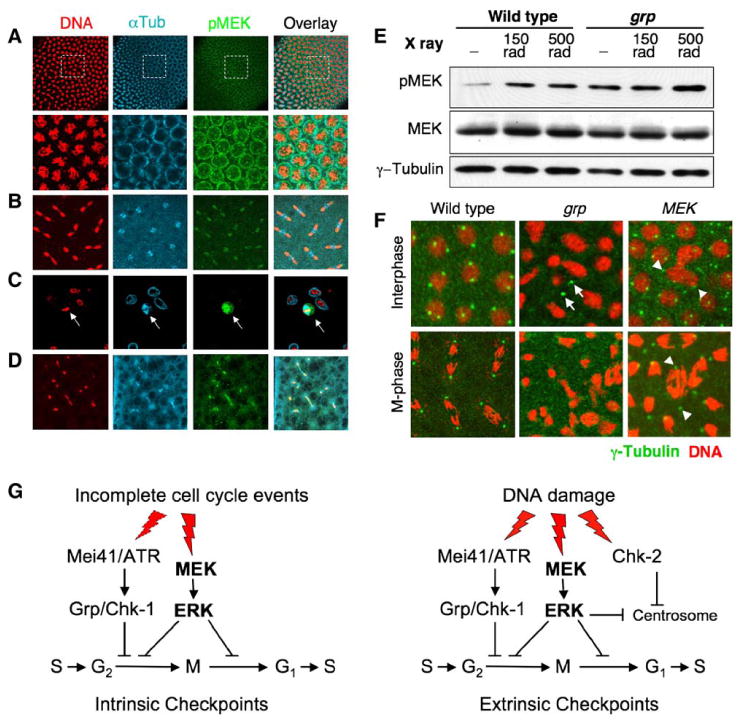
(A) A division cycle-12 wild-type embryo was fast-fixed and stained with indicated antibodies. Note that a band of higher pMEK signals (green) was seen coinciding with prophase or late interphase nuclei. Lower panels: higher magnification of boxed areas of top panels.
(B) A cycle-10 wild-type embryo during anaphase/telophase.
(C) An S2 cell during mitosis (arrow).
(D) A cycle-9 grp embryo during anaphase/telophase.
(E) Wild-type and grp mutant embryos were irradiated with 0, 150, or 500 rad of X-ray, immediately subjected to SDS-PAGE, and blotted sequentially with indicated antibodies. Note the increased pMEK levels in irradiated embryos, and in grp mutant embryos even without irradiation (cf. lanes 1 and 4).
(F) Chk2-dependent centrosome inactivation fails in MEK embryos. Cycle-13 embryos of indicated genotypes were stained for DNA (red) and γ-tubulin (green). Note the centrosome foci (bright green spots) present in wild-type and MEK embryos but absent in grp embryos. Arrows point to free centrosome foci not associated with the nucleus in the grp embryo. Arrowheads point to centrosome foci associated with morphologically abnormal nuclei or chromosomes in the MEK embryo.
(G) A model for the MEK/ERK pathway in cell cycle checkpoints. Cell cycle checkpoints are regulatory mechanisms that can be classified as intrinsic (left) and extrinsic (right) pathways. The intrinsic pathways ensure the orderly progression of cell cycle events and are activated at different transition points to prevent premature entry into the next cell cycle event. Activation of the MEK/ERK pathway at entry into and exit from mitosis represents such an intrinsic checkpoint regulatory mechanism. The ATR/Chk1 pathway may act in conjunction with MEK. The extrinsic pathways are activated only when DNA damage is detected. The MEK/ERK pathway acts in conjunction with or in parallel to the Chk1 and Chk2 pathways to halt the cell cycle progression in response to DNA damage.
