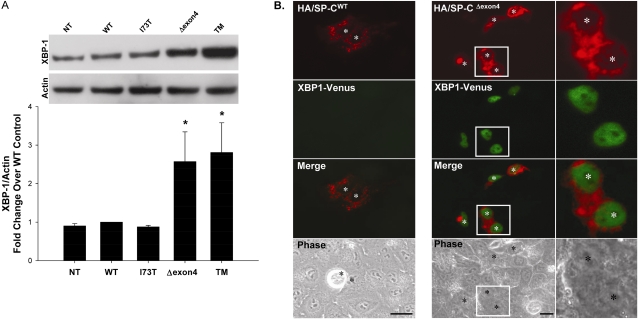
Figure 2.
SP-C BRICHOS mutants activate the insulin response element 1 (IRE1) signaling pathway. (A) A549 cells, either nontransfected (NT) or transiently transfected with the indicated control or EGFP–SP-C constructs (WT, I73T, Δexon4 were harvested 48 hours after transfection. Overnight treatment with 10 μg/ml tunicamycin (TM) was used for a positive control sample. Cell lysates were analyzed for XBP-1 protein expression by Western blotting, as described in Materials and Methods. An anti–β-actin antibody was used as a loading control. A representative immunoblot appears above the graph. Band intensities were quantified by densitometry, and the ratio of XBP-1 to β-actin was determined. Data are expressed as fold change over WT control, and represent the mean ± SD of three separate experiments. *P < 0.05 versus WT control. (B) Hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged SP-CWT (left) or SP-CΔexon4 (right) were cotransfected with the ERAI plasmid (XBP-1/venus) developed by Iwawaki and colleagues (14) into A549 cells. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were fixed and stained with an anti-HA monoclonal antibody to label the HA–SP-C fusion protein, as described in Materials and Methods. Fluorescence microscopy shows XBP-1/venus expression in SP-CΔexon4 but not in SP-CWT transfected cells. Merged and phase contrast images are shown, and individual nuclei are identified by asterisks. Magnifications of selected areas are seen in the rightmost column.