Fig. 1.
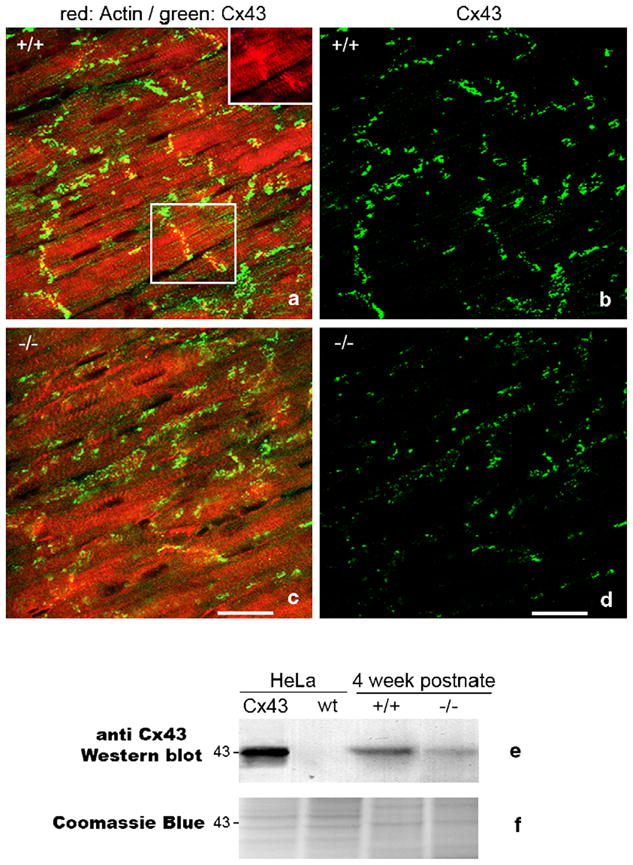
Spatial heterogeneities in ventricular Cx43 in HF-1b knockout myocardium. (a–d) Double labeling for Cx43 (green) and rhodamine–phalloidin (red) in posterior apical myocardium of the ventricle of the HF-1b wildtype (a) and knockout (c). The inset in the upper right corner of (a) shows rhodamine–phalloidin delineation of intercalated disks shown in the boxed region within (a). Rhodamine–phalloidin labeling was used in the identification and quantification of percent Cx43 area localized at intercalated disks (see Table 1). (b, d) Cx43 signal from images in (a) and (c) are shown without rhodamine–phallodin staining to improve illustration of the differences in Cx43 level and distribution between wildtype and knockout tissues. Scale bars=25 μm. (e) Cx43 Western blots of wildtype (non-Cx43 expressing) HeLa cells and HeLa cells stably transfected with Cx43, ventricular myocardium (VM) of 4-week postnate HF-1b knockout and wildtype littermates. (f) Coomassie blue-stained gel equivalent to those transferred to membrane for probing with Cx43 antibody shows equal loading of lanes.
