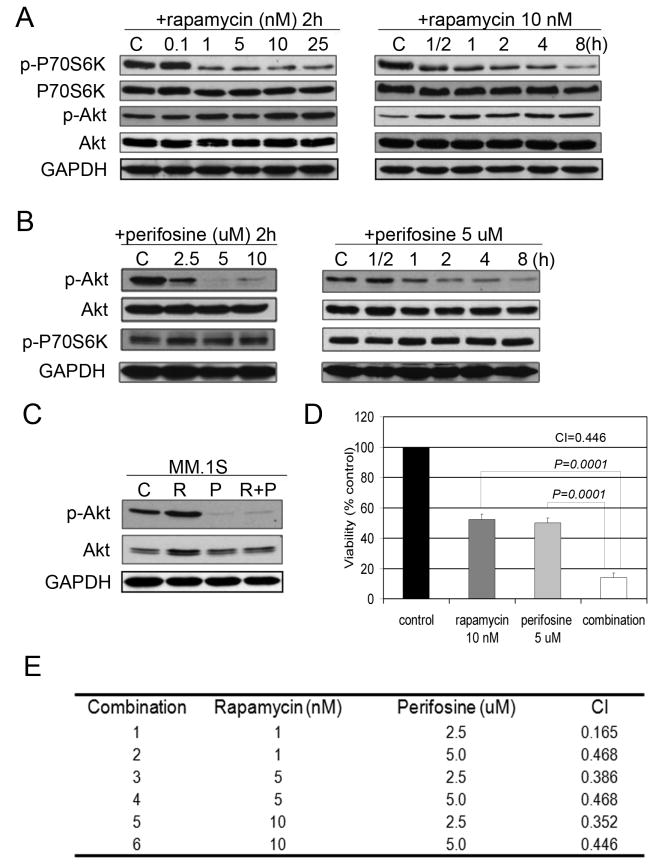
Fig. 1. Rapamycin induces p-Akt in MM cells, while perifosine inhibits Akt.
(A) MM.1S cells were incubated with culture media or rapamycin (0.1-25 nM) for 2 hours, or rapamycin (10 nM) for the indicated periods. Whole-cell lysates were subjected to western blotting using anti-p-P70S6K, anti-P70S6K, anti-p-Akt, or anti-Akt antibodies.
(B) MM.1S cells were incubated for 2 hours with culture media, or perifosine (2.5-10 uM), or perifosine (5 uM) for the indicated time points. Whole-cell lysates were subjected to western blotting using anti-p-P70S6K, anti-P70S6K, anti-p-Akt, or anti-Akt antibodies.
(C) MM.1S cells were cultured for 6 hours in control media (C), rapamycin 10 nM (R), perifosine 5 uM (P), or rapamycin and perifosine (R+P). Whole-cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting using anti-p-Akt and anti-Akt antibodies.
(D) MM.1S cells were cultured for 48 hours in control media, rapamycin, perifosine, or their combination as indicated. Cytotoxicity was assessed by MTT assay.
(E) MM.1S cells were cultured at varying concentrations of rapamycin (1, 5, 10 nM) with perifosine (2.5, 5 uM) and cytotoxicity evaluated by MTT assay at 48 hours. Combination index (CIs) was calculated based upon the isobologram generated using the Chou-Talalay method.