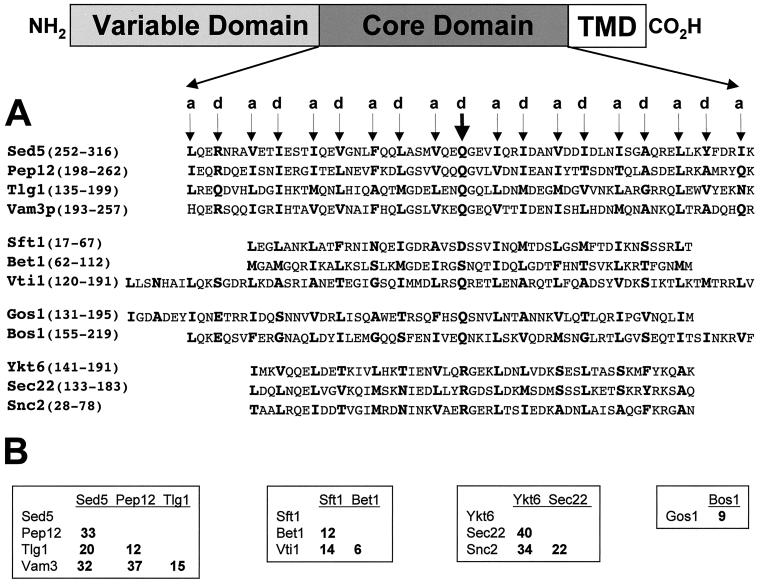
Figure 1.
(A) Amino acid sequence alignments of the heptad repeat/core domains of the SNAREs used in these studies. The a and d positions of the predicted hydrophobic layers (heptad repeats) are indicated above the arrows and the amino acids at these positions are highlighted in bold. The thick arrow indicates the position of the d amino acid, which has been used to define proteins as either R- or Q-SNAREs (Fasshauer et al., 1998). This position also corresponds to the zero ionic layer in the structure of the neuronal SNARE complex (Sutton et al., 1998). SNARE proteins are aligned with their putative family members: the syntaxins (Sed5p, Pep12p, Vam3p, and Tlg1p), the Bet1 family (Sft1p, Bet1p, and Vti1p), the Gos1p family (Gos1p and Bos1p), and the synaptobrevin family (Ykt6p, Sec22p, and Snc2p). The position of the amino acids in each of the proteins used in the alignments, is indicated in parentheses. The assignment of SNAREs to a particular family is based in part on amino acid sequence similarity as well as on the behavior of individual SNARE proteins in in vitro mixing assays (see text for details). (B) Pairwise percentage of amino acid identities among the aligned SNARE family proteins as indicated in A.