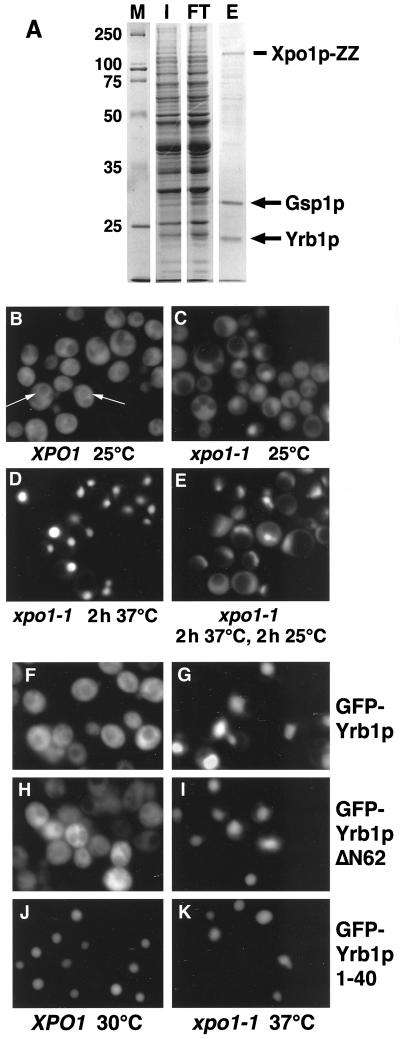
Figure 1.
(A) Yrb1p is a major Xpo1p-binding protein. Xpo1p-ZZ was purified from yeast extracts in the presence of recombinant Gsp1pQ71L-GTP as described in Materials and Methods, and proteins bound to immobilized Xpo1p were eluted with 500 mM KCl. The input (I), flow-through (FT), and eluate (E) were analyzed by SDS PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. The two major proteins in the eluate were identified by MALDI and Western blotting and correspond to Gsp1p and Yrb1p. Molecular weight markers (M) are in kDa. (B-E) Yrb1p shuttles between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Wild-type cells (B) or xpo1–1 cells (C-E) expressing GFP-YRB1 were grown in liquid medium at 25°C. The cultures were kept at 25°C (C), shifted to 37°C for 2 h (D), or shifted to 37°C for 2 h and then shifted back to 25°C for 2 h (E). To inhibit protein synthesis, cycloheximide (final concentration 0.1 mg/ml) was added to the cultures before the temperature shift. The cells were viewed by fluorescence microscopy to visualize GFP-Yrb1p. The perinuclear staining in wild-type cells is indicated by arrows. (F-K) Yrb1p has two nuclear targeting sequences. Wild-type cells (F, H, and J) or xpo1–1 mutants (G, I, and K) were transformed with plasmids encoding GFP-Yrb1p, GFP-Yrb1ΔN62p, or GFP-Yrb1p 1–40, as indicated. The cultures were incubated at 30°C (XPO1 cells) or 25°C (xpo1–1 cells) in raffinose-containing medium. Expression of the GFP fusions was induced by 2% galactose and repressed by addition of 2% glucose after 1 h. Cells were kept at 30°C (XPO1) or shifted to 37°C for 2 h (xpo1–1) and viewed by fluorescence microscopy.