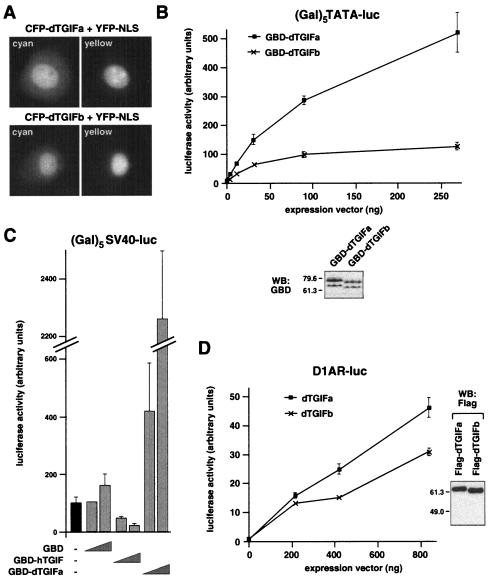
FIG. 5.
dTGIFa and dTGIFb are transcriptional activators. (A) dTGIFs are nuclear. Fusion proteins consisting of amino-terminal fusions of eCFP to either dTGIFa or dTGIFb were coexpressed in COS-1 cells with an eYFP-NLS protein to mark the nucleus. Individual cyan and yellow images are shown. (B) The full-length coding sequence of either dTGIFa or dTGIFb was fused to the GBD. Increasing amounts of GBD-dTGIF fusions were coexpressed in L17 cells transfected with a luciferase reporter in which the luciferase gene is activated by a minimal TATA element and multiple Gal4 binding sites. Relative expression of the maximum levels of transfected GBD-dTGIF fusions was assayed by Western blotting (WB) with an antibody against the GBD as shown below. (C) GBD, GBD-dTGIFa, or GBD-TGIF expression vectors (10 or 100 ng per well) were cotransfected into HepG2 cells with a (Gal)5-SV40 luciferase reporter, and luciferase activity was assayed as described for panel B. (D) L17 cells were cotransfected with increasing amounts of Flag-dTGIF expression vectors and a D1AR-luc reporter, in which the D1AR promoter drives luciferase expression. Relative expression levels of the Flag-dTGIFa and dTGIFb proteins are shown by Western blotting. Luciferase activity (mean ± standard deviation of triplicate transfections) is shown in arbitrary units.