FIG. 3.
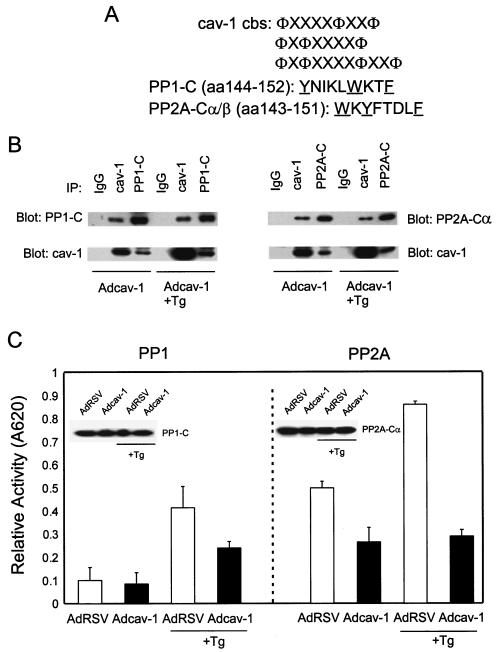
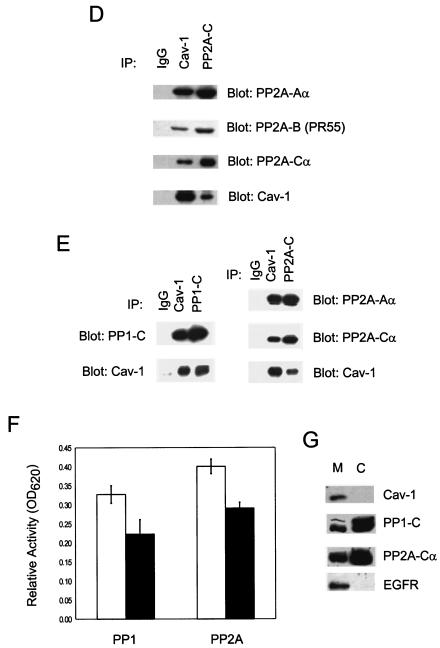
cav-1 interacts with and inhibits PP1 and PP2A. (A) cav-1 consensus binding sites (cbs) and putative cav-1 binding sites in catalytic (C) subunits of PP1 and PP2A. Aromatic residues (Φ) and any amino acid (X) in the cav-1 consensus binding sites are indicated. The aromatic residues in PP1-C and PP2A-C are underlined. aa, amino acids. (B) Analysis of IP complexes of cav-1, PP1-C, and PP2A-Cα in Adcav-1-infected LNCaP cell lysates showing that cav-1 coprecipitates with PP1-C or PP2A-Cα. (C) Serine/threonine protein phosphatase assay using PP1-C or PP2A-Cα IP complexes, indicating that cav-1 inhibits PP1 and PP2A activities. Relative activity was determined by measuring the absorbance at 620 nm (A620). The protein expression levels of PP1-C and PP2A-Cα in the same cell lysates are shown in the blot inserts. (D) Detection of two other subunits of PP2A (PP2A-Aα and PP2A-B) in cav-1 or PP2A-Cα IP complexes. (E) Analysis of cav-1 and PP1-C IP complexes after the interaction of purified cav-1 protein with the catalytic subunit of PP1 in vitro (left), and analysis of cav-1 or PP2A-Cα IP complex after the interaction of purified cav-1 protein with PP2A core enzyme in vitro (right). Note that cav-1 interacts with the C subunit of PP1 outside the context of holoenzyme and cav-1 interacts with PP2A in its core enzyme form. (F) Purified cav-1 protein inhibits PP1 and PP2A activities in vitro. Cells were treated with purified cav-1 (▪) or not treated with purified cav-1 (□). Relative activity was determined by measuring the optical density at 620 nm (OD620). (G) Distribution of cav-1, PP1, and PP2A in the microsomal fraction (M) (100,000 × g pellet) and cytosol fraction (C) (100,000 × g supernatant). EGFR was used as a marker for the plasma membrane.