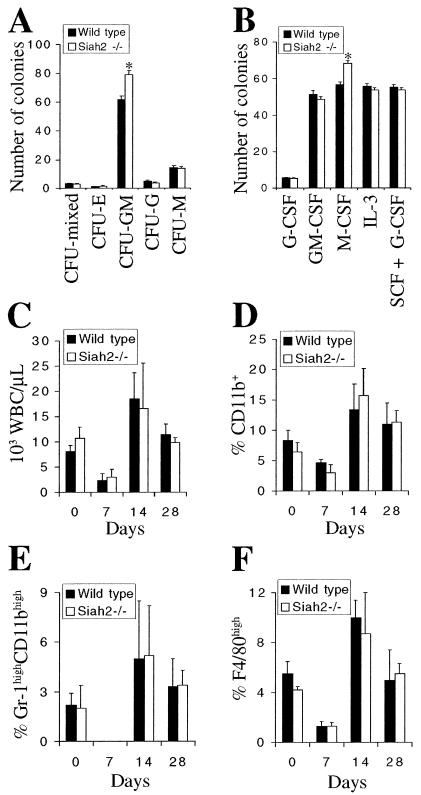
FIG. 3.
Expansion of myeloid progenitors in Siah2 mutant mice. (A) Twelve-day methylcellulose colony-forming cell assay of bone marrow from wild-type and Siah2−/− mice. Bone marrow was obtained from six mice of each genotype, and each sample was cultured in duplicate with IL-3 (1,000 U/ml), IL-6 (1,000 U/ml), SCF (approximately 100 ng/ml), and erythropoietin (2 U/ml). Colony type was assigned based on distinctive morphology, and mean colony numbers are shown (error bars, standard errors of the means). *, statistically significant difference between genotypes (P < 0.00003; Student's t test). (B) Seven-day agar colony-forming cell assay of bone marrow from wild-type and Siah2−/− mice. Bone marrow was obtained from six mice of each genotype, and each sample was cultured in duplicate. Data represent mean numbers of colonies (error bars, standard errors of the means) after 7 days of culture with either G-CSF (1,000 U/ml), GM-CSF (1,000 U/ml), M-CSF (20 ng/ml), IL-3 (1,000 U/ml), or SCF (approximately 100 ng/ml) and G-CSF (1,000 U/ml). *, statistically significant difference between genotypes (P < 0.001; Student's t test). (C to F) Hematopoietic recovery assay after intraperitoneal injection of wild-type and Siah2−/− mice with 5-fluorouracil (150 mg/kg of body weight). Peripheral blood was analyzed at the time of injection (day 0) and 7, 14, and 28 days after injection for total white blood cell counts (C), percentage of white blood cells expressing the common myeloid marker CD11b (D), high levels of Gr-1 and CD11b (markers of mature granulocytes) (E), or high levels of F4/80 (marker of macrophages) (F). Data represent means + standard deviations (error bars) from analysis of five wild-type and four Siah2−/− mice.