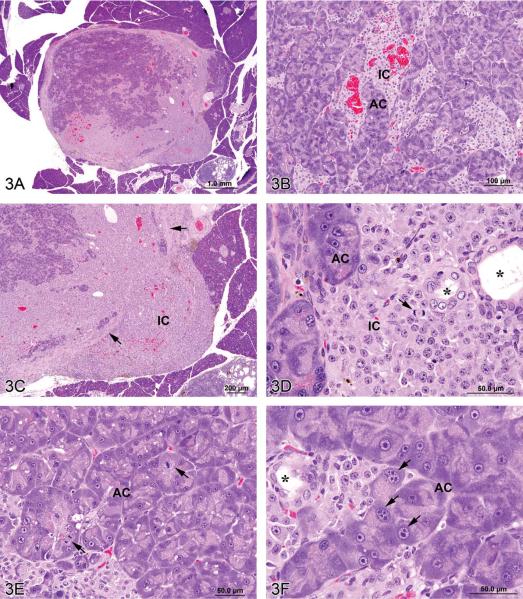
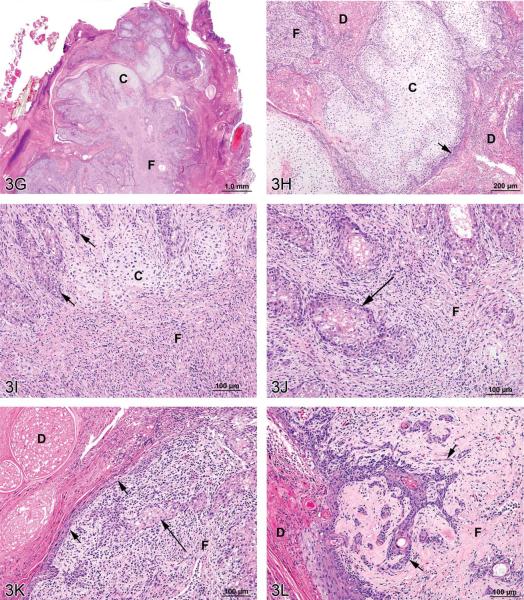
Figure 3.
Mixed tumors in the rat. (A) Pancreatic malignant mixed tumor from a male F344/N rat from a 2-year bioassay. (B) Higher magnification of the neoplasm in (A) showing intermingled but distinct acinar cell (AC) and islet cell (IC) components. (C) Extension of neoplastic IC across the fibrous capsule (arrows). (D) Neoplastic IC are pleomorphic and may have mitotic figures (arrow). Ductules (*) are lined by epithelial cells with abundant pale pink cytoplasm and large vesicular nuclei. (E) Pleomorphic neoplastic AC have abundant cytoplasm with decreased zymogen granules and sometimes mitotic figures (arrows). (F) Neoplastic AC are also characterized by large, vesicular nuclei with prominent, often multiple nucleoli (arrows). Ductules (*) are lined by epithelial cells with abundant pale pink cytoplasm and large vesicular nuclei. (G) Preputial gland from a male F344/N rat from a 2-year bioassay. Extensive areas of cartilaginous (C) and fibrous (F) tissues compress and replace the normal glandular architecture. (H) Higher magnification of the mass exhibits cartilage (C) and fibrous connective tissue (F). Dilated ducts (D) are filled with necrotic debris, inflammatory cells, and keratin and lined by poorly differentiated epithelial cells (arrow). (I) Areas of cartilage (C) and fibrous connective tissue (F) in which are scattered acinar-like structures (arrows). Diffuse inflammatory cell infiltrates are present in the fibrous tissue (F). (J) Fibrous connective tissue (F) contains diffuse inflammatory cell infiltrates and surrounds poorly differentiated acinar-like structures (arrow). (K) Fibrous connective tissue (F) contains diffuse inflammatory cell infiltrates and surrounds poorly differentiated acinar-like structures (long arrow). The adjacent dilated duct (D) is distended by necrotic debris, keratin, and inflammatory cells and is lined by poorly differentiated squamous epithelium (short arrows). (L) The poorly differentiated squamous epithelium lining a dilated duct (D) exhibits extension of branching cords and “dropping off” of cell clusters and individual neoplastic cells (arrows) into the underlying fibrous connective tissue (F). H&E.