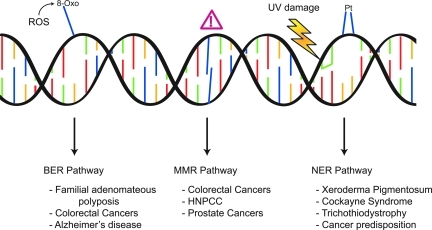
FIG. 1.
DNA damage excision repair pathways and the diseases related to dysfunctional repair of the lesions. The BER pathway recognizes and removes modified bases resulting from endogenous ROS, deamination, or alkylation. The MMR pathway is responsible for recognition and repair of misincorporated bases that occur during replication. The NER pathway repairs damage that occurs to DNA due to exogenous sources, primarily CPDs and 6-4 photoproducts, which form in response to UV exposure. In addition, the NER pathway is the primary repair pathway for repair of 1,2-d(GpG) and 1,3-d(GpNpG) cisplatin adducts. While all excision repair pathway deficiencies are associated with an increase risk and predisposition to cancer, BER deficiencies have been linked to Alzheimer's disease, and NER deficiencies are associated with XP, CS, and TTD. (To see this illustration in color the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertonline.com/ars).