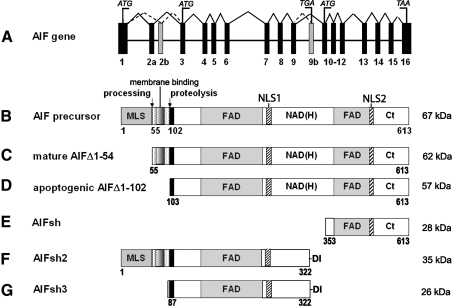
FIG. 1.
Major forms and splice variants of AIF. (A) Schematic representation of the human AIF gene. Exons are numbered; alternative exons giving splice variants are in gray. Translation initiation (ATG) and stop codons (TGA/TAA) are indicated. (B, E–G) Naturally occurring transcripts corresponding to the AIF precursor, AIFsh, AIFsh2, and AIFsh3, respectively. (C) Mature form of AIF produced upon mitochondrial processing. Depending on the usage of exons 2a and 2b, the ubiquitously expressed AIF1 or brain-specific AIF2 isoforms can be synthesized. (D) Truncated apoptogenic form produced in the intermembrane space upon proteolytic processing. The FAD-binding, NAD(H)-binding, and C-terminal (Ct) domains are indicated. AIF, apoptosis-inducing factor; MLS, mitochondrial leading sequence; NLS, nuclear leading sequence.