FIG. 1. .
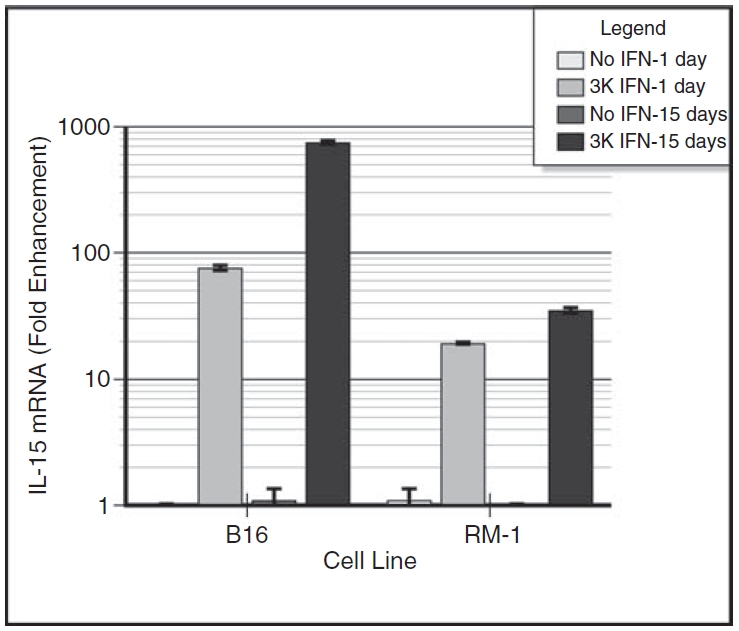
Induction of interleukin-15 (IL-15) mRNA by interferon-α (IFN-α) treatment of B16α cells and RM-1α cells. Monolayers of B16α and RM-1α cells were grown in medium containing 3,000 units/mL of IFN-α for 1 day or for 15 days. Control monolayers of B16 parental cells were given medium alone without IFN treatment. At 1 day after providing fresh medium with or without IFN-α, the cells were lysed and the RNA harvested was subjected to real-time RT-PCR. The levels of IL-15 mRNA and GAPDH mRNA were determined. After adjusting for the levels of GAPDH mRNA in each of the preparations, the level of IL-15 mRNA in parental cells grown in medium alone was set at 1 and the level of IL-15 mRNA in IFN-treated cells was expressed as fold enhancement. The data are expressed as fold enhancement (mean ± SE) in IL-15 mRNA level versus days of IFN treatment. Student’s t-test analysis: day 1 B16 parental cells versus day 1 B16α cells: P < 0.0001; day 1 RM-1 parental cells versus day 1 RM-1α cells: P < 0.0001; day 15 B16 parental versus day 15 B16α cells: P < 0.0001; day 15 RM-1 parental cells versus day 15 RM-1α cells: P < 0.0001; day 1 B16α cells versus day 15 B16α cells: P < 0.0001; day 1 RM-1α cells versus day 15 RM-1α cells: P < 0.0018.
