Figure 3.
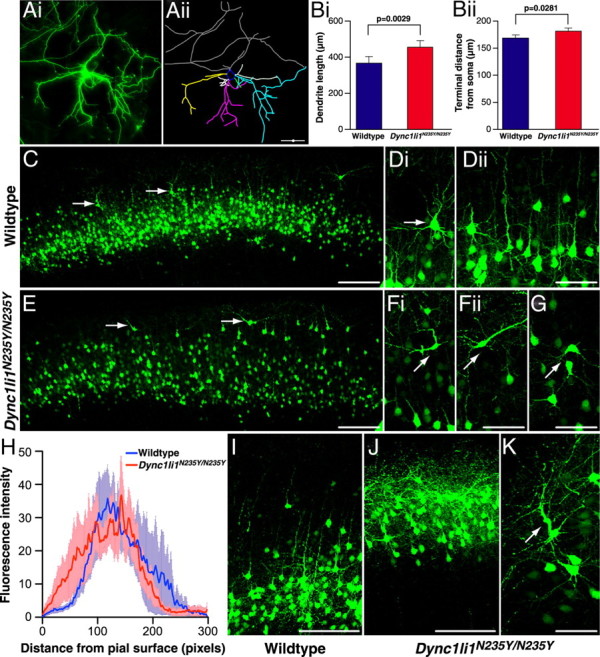
Morphology of wild-type and mutant Dync1li1N235Y/N235Y cortical neurons. A, Cortical neurons were electroporated in vivo at E15, then cultured in vitro from E17 embryos. At 10 DIV they were analyzed to compare morphology of wild-type and Dync1li1N235Y/N235Y cortical neurons. GFP-positive neurons (i) were hand-traced using Neurolucida software (ii). B, The length of dendritic trees for wild-type and Dync1li1N235Y/N235Y neurons, in vitro. i, Dync1li1N235Y/N235Y dendrites were significantly longer than in wild-type neurons (p = 0.0029). ii, Dync1li1N235Y/N235Y dendrites terminated significantly further from the soma than wild-type dendrites (p = 0.00281). C, Low magnification of the cortex from a wild-type brain electroporated with GFP at E15 and harvested at P15. GFP-positive neurons occupy a discreet band corresponding to cortical layers II/III. D, i, Higher-magnification image showing the orientation of a pyramidal neuron in layer II. ii, Neighboring neurons align in the same orientation with apical dendrites projecting toward the pial surface. E, The cortex from a Dync1li1N235Y/N235Y brain electroporated with GFP at E15 and harvested at P15 (rostrocaudally matched with C). Compared with C, GFP-positive cells were more distributed, with more neurons residing in the uppermost part of the cortex (arrows). F, The cell body and apical dendrite of neurons located closer to the pial surface in Dync1li1N235Y/N235Y mutants were mis-oriented. G, Neurons in layer II of Dync1li1N235Y/N235Y cortex also often displayed incorrect orientation. H, Comparison of the proportion of electroporated neurons located in upper layers of the neocortex, as measured by fluorescence intensity. I, Higher-magnification imaging from wild-type cortex in more caudal sections showed most GFP-positive neurons within layer II/II. J, In contrast to I, GFP-expressing cells in Dync1li1N235Y/N235Y cortex occupied a location much closer to the pial surface. K, The apical dendrite of neurons Dync1li1N235Y/N235Y cortex were often thickened and projected in an incorrect orientation. Scale bars: A, C, E, I, J, 100 μm; D, F, G, K, 50 μm.
