Figure 1.
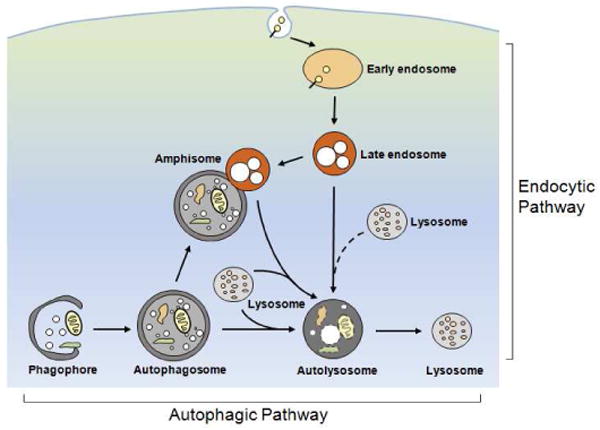
Schematic illustrating the endocytic and the autophagic pathways to the lysosome. Internalized materials entering the endocytic pathway are directed to early endosomes, which mature to late endosomes/multivesicular bodies. In the autophagic pathway, a phagophore sequesters an area of cytoplasm containing organelles to form a double membrane-limited autophagosome. The formation of amphisomes via the fusion between autophagosomes and late endosomes/multivesicular bodies provides an interactive point between the two pathways. Autophagosomes, and amphisomes in the two pathways receive hydrolases by fusing with lysosomes to form autolysosomes or late endosomes/multivesicular bodies to form amphisomes. Efficient digestion of substrates within these compartments yields lysosomes containing mainly acid hydrolases.
