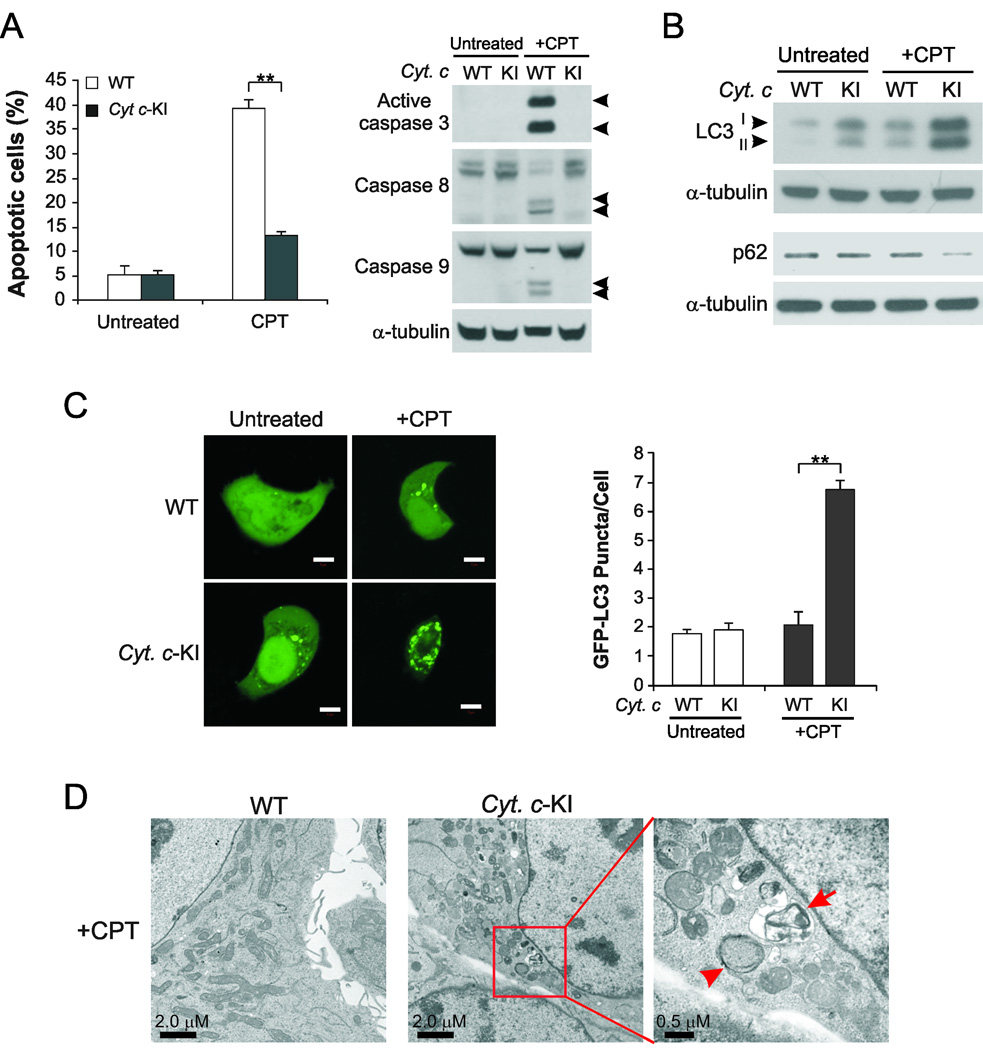
Fig. 1. Induction of autophagy in cytochrome c-mutant knock-in cells.
(A) WT and cytochrome c-mutant-knock-in (Cyt c-KI) HCT116 cells were treated with 500 nM camptothecin (CPT) for 48 hr. Left, apoptosis was analyzed by counting cells with condensed and fragmented nuclei following nuclear staining with Hoechst 33258. **p<0.01. Right, Western blot analysis of caspases 3, 8, and 9. Arrowheads indicate caspase cleavage fragments. (B) Western blot analysis of LC3II accumulation and p62 degradation in WT and Cyt c-KI HCT116 cells treated with CPT for 24 hr. (C) Confocal microscopic analysis of WT and Cyt c-KI HCT116 cells transfected with GFP-LC3, and then treated with 500 nM CPT for 24 hr. Left, representative confocal images. Scale bar: 5 µm. Right, quantification of GFP-LC3 puncta signals. (D) Transmission electron microscopic analysis of WT and Cyt c-KI HCT116 cells treated with 500 nM CPT for 24 hr. Arrowhead indicates an autophagosome with double membrane structure. Arrow indicates an autolysosome with a degraded organelle.