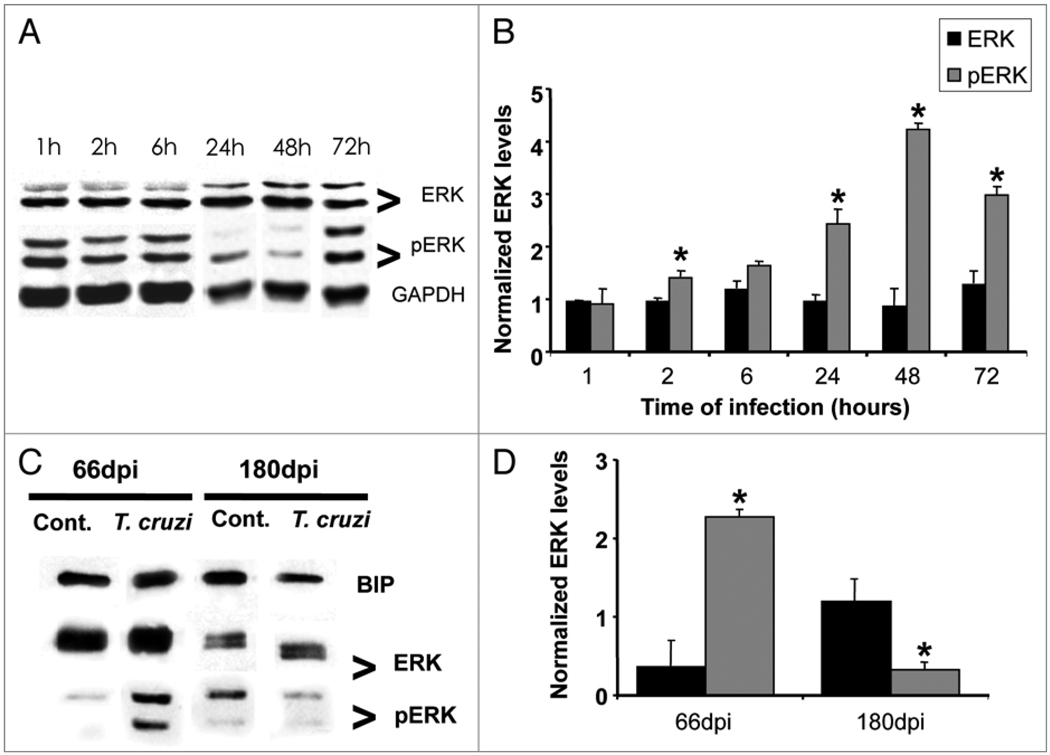
Figure 4.
Trypanosoma cruzi infection induces activation of ERK 1/2 in cultured cardiac myocytes and in the myocardium of infected mice. (A) Cultured cardiac myocytes were infected with T. cruzi and blots were probed against anti-total ERK and pERK. There was no change in total ERK over a 72 hours infection. However, a progressive increase in pERK (activation) over the same period of time was observed. GAPDH (36 KDa) was used as loading control in myocyte samples (n = 3 for each group). (C and D) Hearts obtained from Brazil strain infected mice (66 and 180 days post infection, dpi) were subjected to SDS-PAGE analysis and probed with anti-phosphoERK antibody. T. cruzi infection induced a 2.3-fold increase in pERK (activation) at 66 dpi and a 68% decrease at 180 dpi as compared with age-matched uninfected controls. BIP (78 KDa) was used as loading control for heart tissue samples (n = 4 for each group) (*p < 0.05, ANOVA).