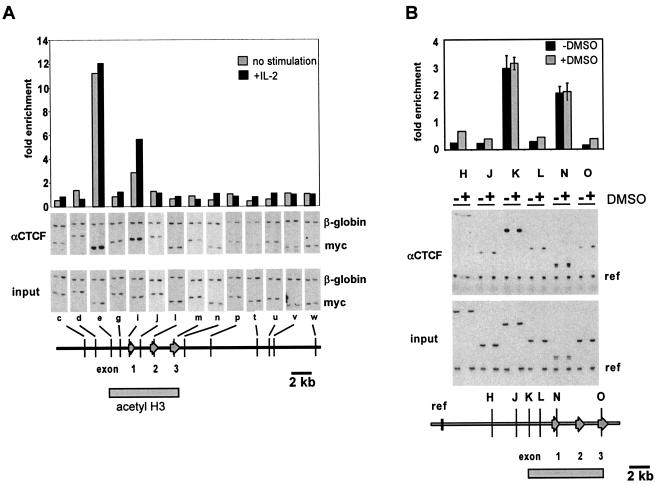
FIG. 2.
CTCF binds in vivo to selected sites of the mammalian c-myc gene loci. ChIP experiments using the anti-CTCF antibody were performed as described in Fig. 1. (A) CTCF binds to the 5′ boundary as well as to the P2 promoter region (e and i) in both resting and IL-2-induced CTLL2 cells. Signals obtained with the murine c-myc primer sets (c to w) are normalized to the signal obtained by the murine β-globin primer set. The degree of enrichment is calculated relative to the ratio obtained in the input DNA fraction as in Fig. 1. (B) CTCF binds to the homologous regions of the human c-myc gene (primer sets K and N). Binding of CTCF is constitutive and not affected by the DMSO-induced inhibition of transcriptional elongation. Note that the 3′ boundaries of the hyperacetylated c-myc regions (grey bar at bottom of figures) are not occupied by CTCF. The data shown for the human c-myc gene are averages from two independent ChIP experiments with independently prepared chromatin derived from HL60 cells, with error bars indicating the standard deviation. The data shown for the murine c-myc gene represent a single representative ChIP.