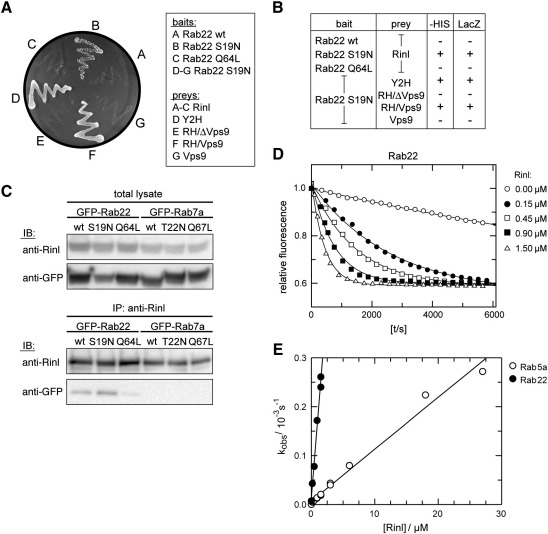
Fig. 5.
Rinl preferentially interacts with GDP-bound Rab22 and acts as GEF for Rab22. (A) Yeast was transformed with Rab22 bait constructs (wt, S19N, Q64L) and Rinl full-length or deletion prey plasmids. Growth on –HIS is shown. (B) The interaction between Rab22 and Rinl was assayed by growth on –HIS and LacZ expression (β-gal assay). (C) Extracts of transiently transfected HEK 293T cells were used to immunoprecipitate Rinl with anti-Rinl antibodies. Co-immunoprecipitated Rab22 was detected by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-GFP. Rab7a was used as negative control. 10% of the input is shown in the top panel (total lysate). (D) 200 nM of mGDP loaded Rab22 were incubated with increasing amounts of Rinl in the presence of 20 μM unlabeled GDP. The exchange of mGDP for GDP was measured in real time as decay in fluorescence signal. (E) The velocity of the nucleotide exchange reaction (kobs) toward Rab5a and Rab22 were determined and plotted against the concentration of Rinl.