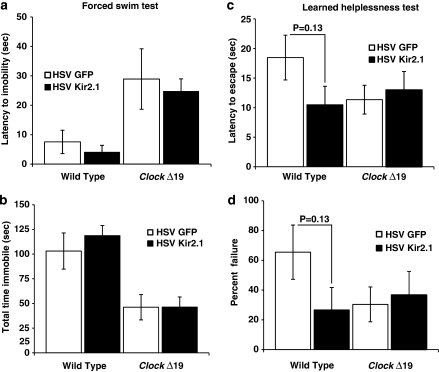
Figure 6.
Depression-like behavior of ClockΔ19 mice is not affected by herpes simplex virus (HSV)-Kir2.1 infection (a, b) HSV-injected ClockΔ19 and wild-type (WT) mice were subjected to the forced swim test (FST). (a) Latency to immobility was determined when the first cessation of all movements occurred for 3 s. There was no difference in latency to immobility observed between HSV-Kir2.1- and HSV-green fluorescent protein-infected mice (n=9–20). (b) Total immobility in the FST was measured and there were no difference in total time immobile between HSV-Kir2.1- and HSV-GFP-injected mice (n=10–20). Both latency to immobility and total time immobile is significantly different between wild-type and ClockΔ19 mice injected with HSV-GFP (P<0.01 by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)). (c, d) ClockΔ19 and WT mice were subjected to the learned helplessness paradigm. (c) The latency to escape was not significantly different between the HSV-Kir2.1- and HSV-GFP-injected mice. (d) The number of escape failures was calculated and there was no significant difference between HSV-Kir2.1- and HSV-GFP-injected mice. (n=6–10).