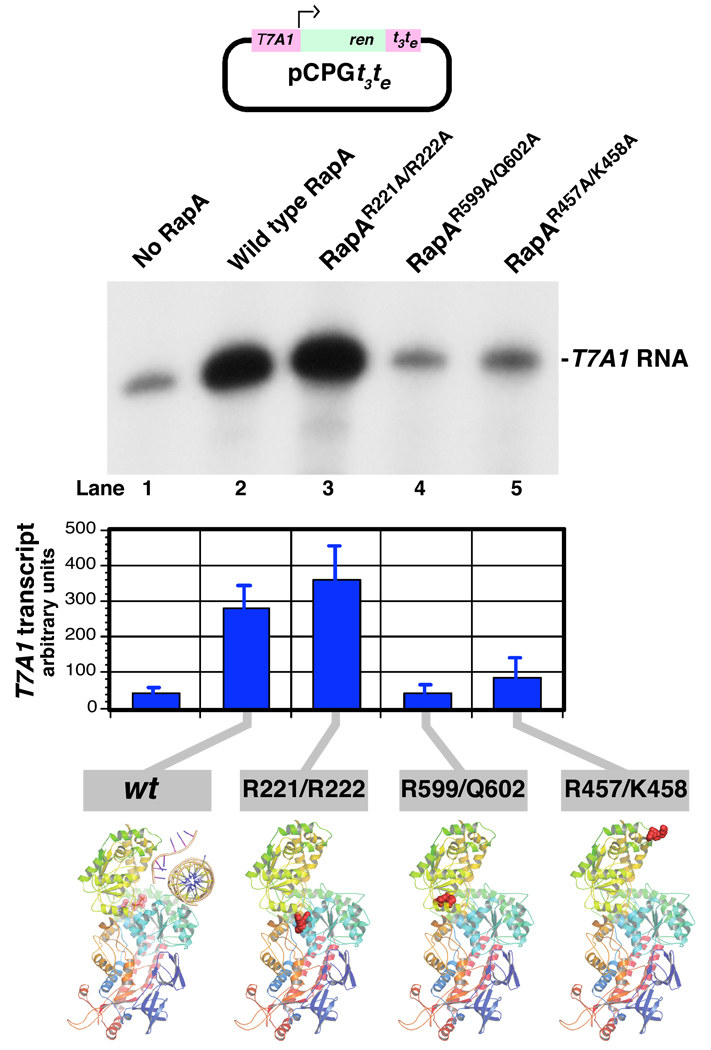
Figure 3. Effect of the mutations in RapA’s SWI/SNF domain and its interface with the putative double-stranded nucleic acid-binding domain on RapA’s transcription-stimulatory activity.
In vitro transcription reactions with the supercoiled DNA template pCPGt3te (26) containing the T7A1 promoter were carried out in Buffer C for 60 min in the absence (lane 1) or in the presence of 0.36 µM recombinant wild-type (lane 2) or mutant RapA proteins (lanes 3–5) as described in Materials and Methods. Supercoiled DNA template, 0.032 µg/µl; purified RNA polymerase holoenzyme, 0.023 µg/µl. Following the addition of Stop solution, the reactions were denatured by boiling and the 32P-labeled RNA transcripts were fractionated on 8% SequaGel (National Diagnostics). Quantitated results of the experiment are shown at the bottom; data represent the average of two independent sets of experiments.