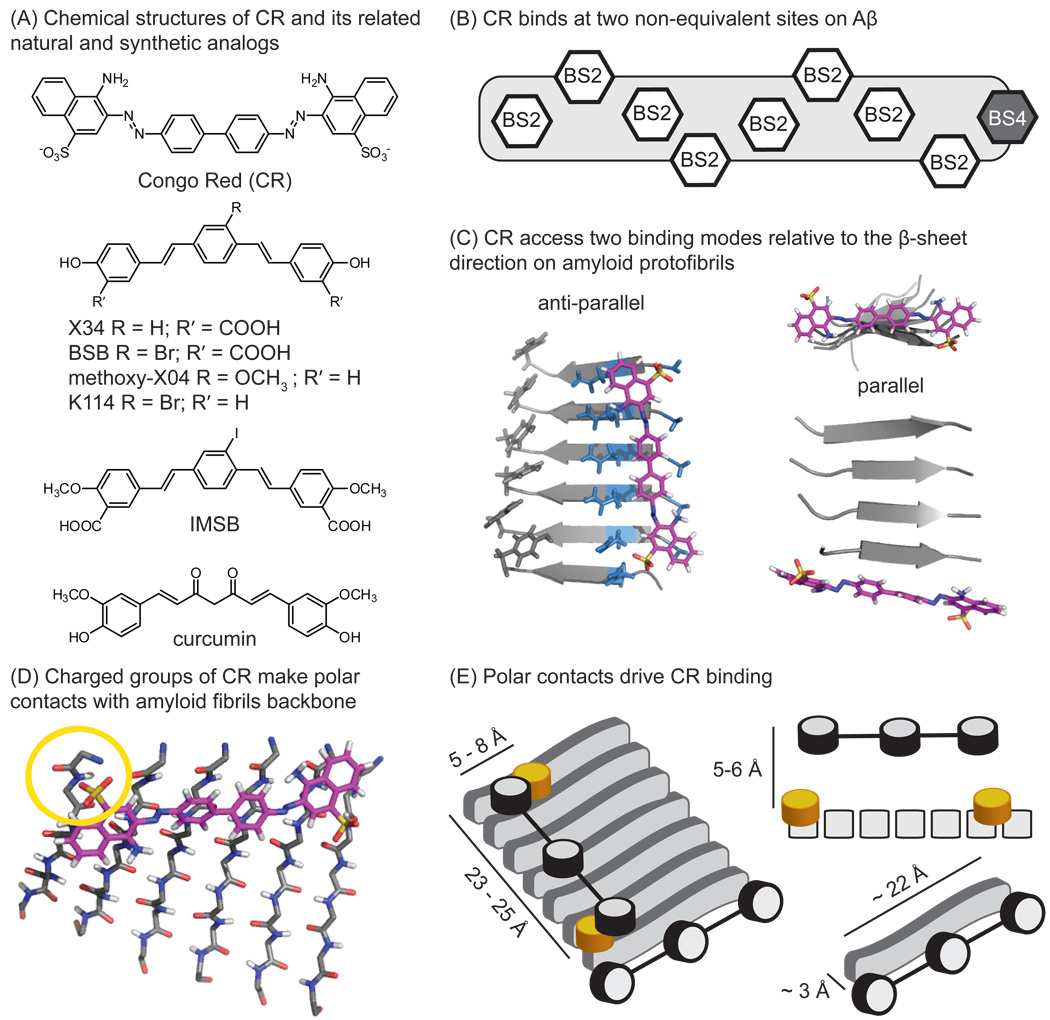
Figure 3. Congo Red (CR) accesses two distinct binding sites on amyloids.
(A) Structures of CR and its analogs. (B) The two CR binding sites on amyloid are shown, one with high density (BS2) and the other with low density (BS4). (C) Model of the high density site, parallel to the fibril axis, and the low density site at the end of the fibril. In the high density site (BS2), the channel is largely composed of polar, uncharged residues. (D) Close-up of the BS2 site, highlighting the interaction with the charged sulfonic acid at the end of the CR molecule. Adapted from [28]. (E) Schematic model of bound CR in the BS2 site, with the molecular dimensions and features shown.