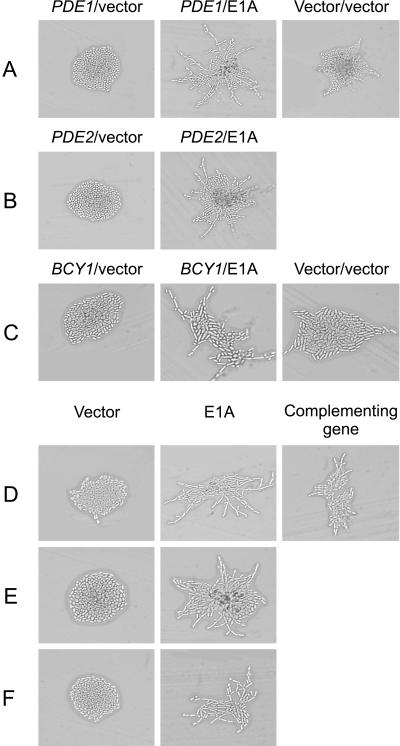
Figure 5.
Ability of the C-terminal domain of E1A to induce pseudohyphal growth in yeast with alterations in the cAMP/PKA signal transduction pathway. The indicated transformants were grown on SLAD medium for 2 d at 30°C and photographed (A–E). Wild-type diploid yeast (JMY38 a/α) were transformed with vectors overexpressing PDE1 (A), PDE2 (B), or BCY1 (C) and either a control vector without E1A (left column) or a vector expressing the C-terminal region of E1A (middle column). Yeast of the same strain transformed with two empty control vectors are shown in the right column. (D–F) Diploid yeast strains with homozygous disruptions of TPK2 (XPY5) (D), FLO8 (XPY95) (E), or FLO11 (XPY107) (F) were transformed with either a control vector without E1A (left column) or a vector expressing the C-terminal region of E1A (middle column). (D) Cells of strain XPY95 transformed with a vector expressing TPK2 are shown in the right column.