Fig. 6.
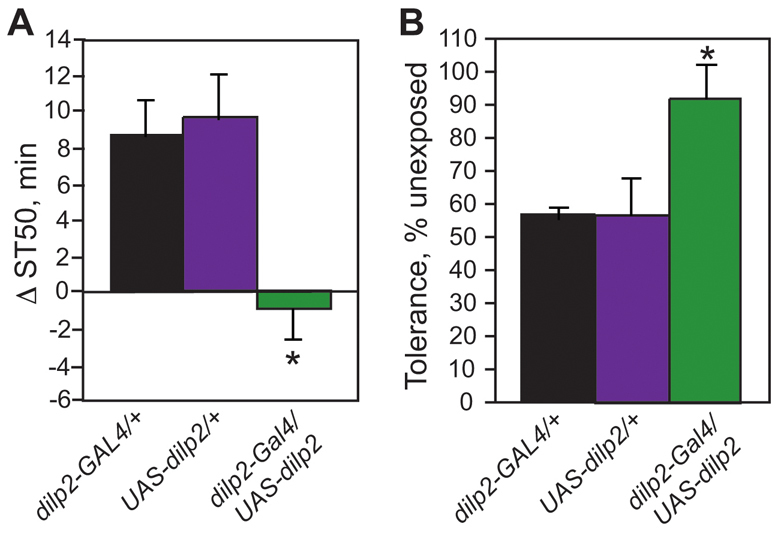
dilp2 expression rescues both sedation resistance and tolerance development. (A) dilp2 expression rescues ethanol-induced sedation resistance. Data are presented as difference in time to 50% sedation (ST50) for ethanol-reared flies as compared with control flies of the same genotype. dilp2-GAL4/UAS-dilp2 flies do not display increased sedation resistance upon ethanol-rearing, whereas both genetic background controls show the expected increase in ST50 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD post-hoc analysis, n=12, *P<0.01). (B) dilp2 expression rescues ethanol-induced tolerance defects. Data are presented as the percent control tolerance (tolerance developed by ethanol-reared flies divided by tolerance developed by control flies of the same genotype multiplied by 100). Although both genetic background controls show a 40–50% reduction in tolerance when reared in ethanol, dilp2-GAL4/UAS-dilp2 flies develop normal levels of ethanol tolerance (one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD post-hoc analysis, n=6, *P<0.05).
