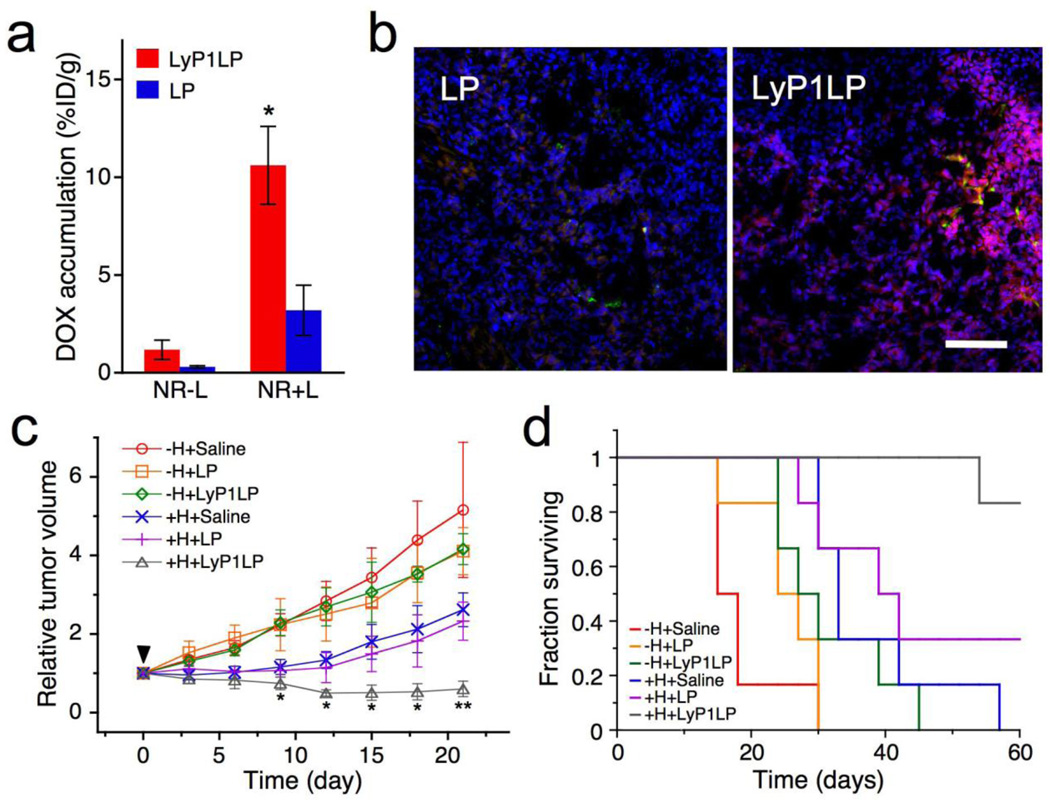
Figure 1.
Enhanced antitumor therapy using near infrared light-heated gold nanorods to up-regulate specific receptors in mice bearing MDA-MB-435 tumors, which are then targeted by a specific ligand on liposomes that contain dox (LyP1LP). (A) Relative accumulation of dox in tumor for targeted (red) vs untargeted (blue) liposomes without heating (NR−L) or with heating (NR+L) to upregulate the receptor. (B) Increased levels of dox (red) are observed in tumors from the mice in (A) subjected to heating (NR+L) when treated with liposomes with (LyP1LP) campared to those without (LP) ligand. Nanoparticles are dyed green; cell nuclei are stained blue. Scale bar is 100 microns. (C) Change in tumor volume of different treatment groups containing bilateral MDA-MB-435 xenograft tumors. 72 hours post-injection of gold nanorods, mice were injected with a single dose of saline, untargeted liposomes (LP) and targeted liposomes (LyP1LP). +H designates one of the two tumors in each animal that was heated. −H designates the tumor that was not heated. (D) Survival rate in different treatment groups after a single 3 mg Dox/kg dose into mice containing a single tumor. Adapted and reproduced with permission from NAS from Figure 4 of Park et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:981–6 (6).