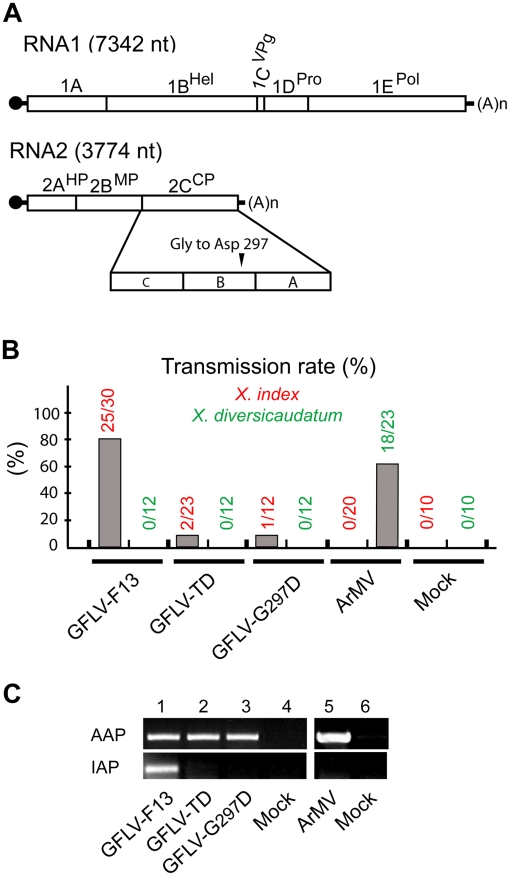
Figure 1. Involvement of capsid protein residue 297 in nematode transmission.
(A) Genomic organization of GFLV. The 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions are denoted by single lines and the VPg is represented by a black circle. Polyproteins encoded by RNA1 and RNA2 are cleaved in five (1A–1E) and three (2A–2C) final maturation products (open boxes), respectively. 1B, helicase (Hel); 1C, viral protein genome-linked (VPg); 1D, protease (Pro); 1E, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (Pol); 2A, homing protein (HP); 2B, movement protein (MP) and 2C, coat protein (CP). As indicated, the CP is composed of three domains called C, B, and A. In the variant GFLV-TD, the CP residue Gly at position 297 is replaced by Asp. (B) Transmission of wild type GFLV-F13, GFLV-TD and GFLV-G297D (the two latter with a Gly297 to Asp297 substitution) and wild type ArMV by X. index and X. diversicaudatum. Transmission rates are expressed as the percentage of ELISA-positive plants. (C) Virus detection in X. index at the end of the AAP and the IAP showed that the mutated viruses and ArMV were ingested but not retained by nematodes. Thirty nematode specimens exposed to source plants infected with GFLV-F13 (lane 1), GFLV-TD (lane 2), GFLV-G297D (lane 3), ArMV (lane 5), or mock inoculated plants (lanes 4 and 6) were randomly collected and tested by RT-PCR with GFLV (lanes 1–4) or ArMV (lanes 5 and 6) specific primers. DNA products were analyzed by electrophoresis on 1.5% agarose gels.