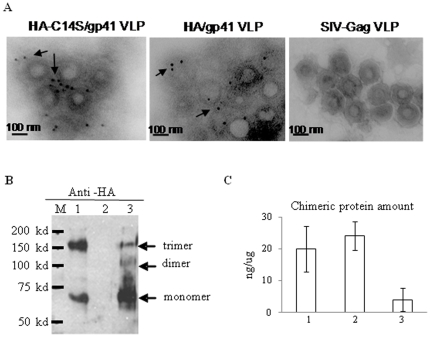
Figure 2. Characterization of the HA/gp41 and HA-C14S/gp41 VLPs.
VLPs were produced in Sf9 insect cells using the recombinant baculovirus expression system and purified through a sucrose gradient as described in Materials and Methods. A. Characterization of VLPs by immune-gold-particle labeling and electron microscopy. Purified HA/gp41, HA-C14S/gp41, as well as the control SIV-Gag VLPs were coated onto a sample grid and then incubated with rabbit-anti-HA antibody Jose4 followed by incubation with gold-particle-conjugated goat-anti-rabbit secondary antibodies. The samples were then fixed with 1% uranyl acetate and then examined under an electron microscope. Arrows indicate gold-particle-labeled glycoproteins on the surface of VLPs. B. Detection of HA/gp41 and HA-C14S/gp41 chimeric protein oligomers in VLPs by Western blot. VLPs were lysed with 1% Triton X-100 and then mixed with non-reducing protein sample buffer followed by analysis by SDS-PAGE coupled with Western blot using antibodies against HA (Jose4). Lane M, molecular weight marker; 1, HA-C14S/gp41 VLP, 2, control SIV Gag VLP; 3, HA/gp41 VLP. C. Determining the amount of HA/gp41 and HA-C14S/gp41 chimeric proteins in VLPs by ELISA. VLPs were lysed with 1% Triton X-100 and then coated onto a microtiter plate at 1 µg per well, and the amount of chimeric proteins were detected by ELISA using rabbit-anti-HA antibody Jose4. Control wells were coated with 1 µg of SIV-Gag VLPs. A standard curve was constructed by coating the wells with serial dilutions of purified HA-histag proteins in mixture with 1 µg SIV Gag VLPs and was used for calculating the amount of chimeric proteins in VLPs.