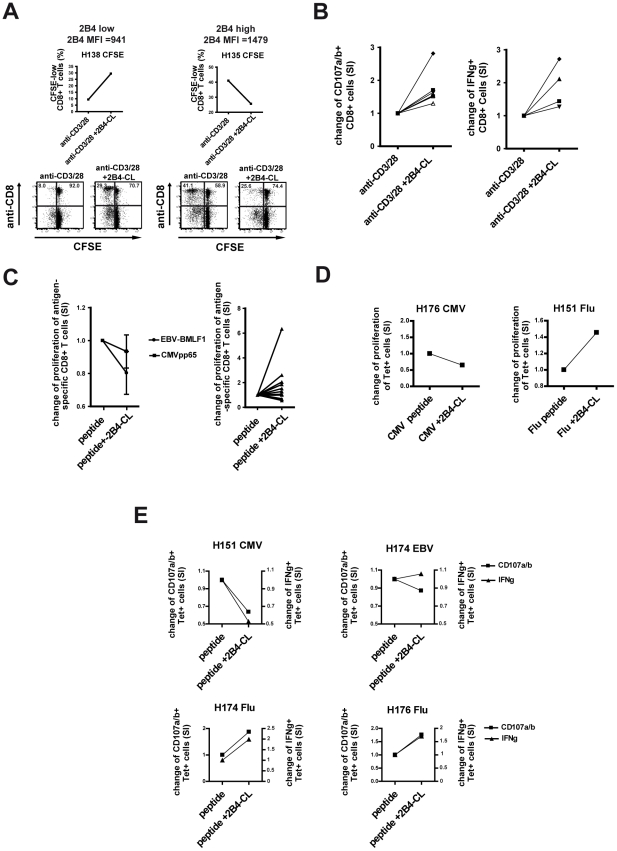
Figure 3. Alteration of CD8+ T cell effector function upon 2B4 cross-linking.
(A) Bulk CD8+ T cells from healthy individuals showed an increase in proliferation upon anti-CD3/28 stimulation and additional 2B4 cross-linking as compared to anti-CD3/28 stimulation alone. This, however, was only the case for cells with a low 2B4 expression level ex vivo (left plots), while cells with high 2B4 expression level ex vivo could not be further enhanced by 2B4 cross-linking (right plots). Ex vivo 2B4 expression levels are indicated above the respective plot. Frequencies of CFSE-low CD8+ T cells are given, representative plots are shown. (B) Additionally, the anti-CD3/28-induced degranulation (as analyzed by CD107a/b expression, left plot) and the IFNγ production (right plot) of bulk CD8+ T cells from healthy individuals with low ex vivo 2B4 expression levels could be enhanced by 2B4 cross-linking in several individuals. Stimulation indices (SI) are shown referring to anti-CD3/28 stimulation alone. (C) Expansion of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells upon peptide-specific stimulation could not be enhanced by additional 2B4-cross-linking in the case of (2B4 high expressing) CMV- or EBV-specific CD8+ T cells (left plot). However, expansion of (low 2B4 expressing) Flu-specific T cells increased upon additional 2B4 cross-linking in most individuals analyzed (right plot). Stimulation indices are shown referring to peptide stimulation alone. (D) Expansion of Flu-specific CD8+ T cells induced by peptide stimulation and additional 2B4 cross-linking is due to an increased proliferation of antigen-specific T cells as seen by a higher frequency of CFSE-low cells. In contrast, CMV- or EBV-specific T cells did not respond to additional 2B4 cross-linking. (E) Degranulation (squares) and IFNγ production (triangles) of CMV- or EBV-specific T cells from healthy individuals did not increase upon 2B4 cross-linking in addition to peptide stimulation (upper panels). In contrast, these effector functions increased upon peptide stimulation and simultaneous 2B4 cross-linking in the case of Flu-specific T cells (lower panels).