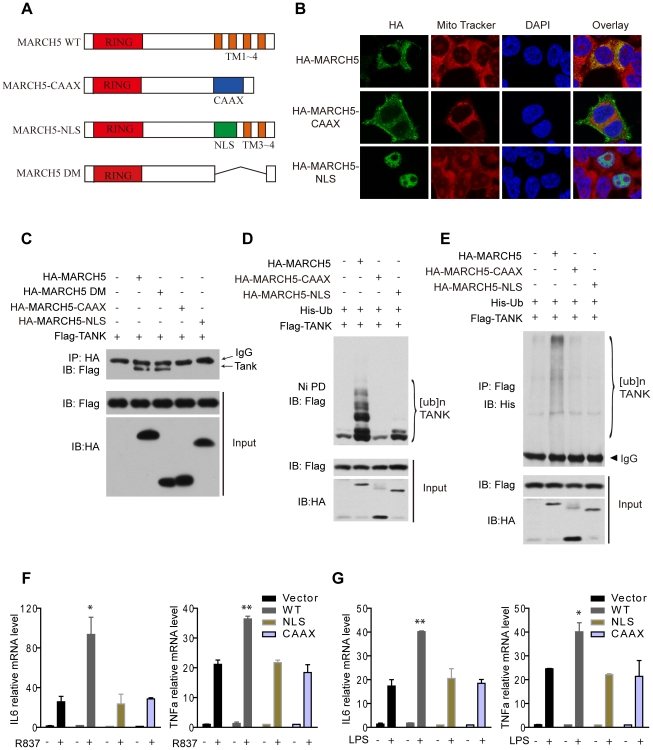
Figure 7. Mislocalization of MARCH5 impairs its function.
A, Schematic diagram of wild-type MARCH5 (MARCH5 WT), its mislocalization mutants and the C-terminal transmembrane domain truncation (Δ105-246 a.a.) (MARCH5-DM); (RING, RING finger domain; TM, transmembrane domain; NLS, nuclear localization sequence). B, HA-MARCH5, HA-MARCH5-CAAX and HA-MARCH5-NLS were transfected into HEK293T cells individually, which were then stained with an anti-HA antibody and imaged by confocal microscopy. The mitochondria were stained with MitoTracker. C, HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated constructs. Then, equal amounts of cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody. The immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with an anti-Flag antibody. D and E, HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cell lysates were subjected to Ni-NTA pulldown (Ni PD) (D) or immunoprecipitation (E) and then immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. F and G, Equal amounts of the indicated Myc-tagged MARCH5 constructs were transfected into Raw264.7 cells. Induction of IL6 and TNFα mRNA by R837 (10 µg/ml) (F) or LPS (100 ng/ml) (G) stimulation was measured by quantitative PCR. Data from F and G are presented as means ± S.D. from three independent experiments. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01. WT, wild type MARCH5; CAAX, MARCH5-CAAX; NLS, MARCH5-NLS.