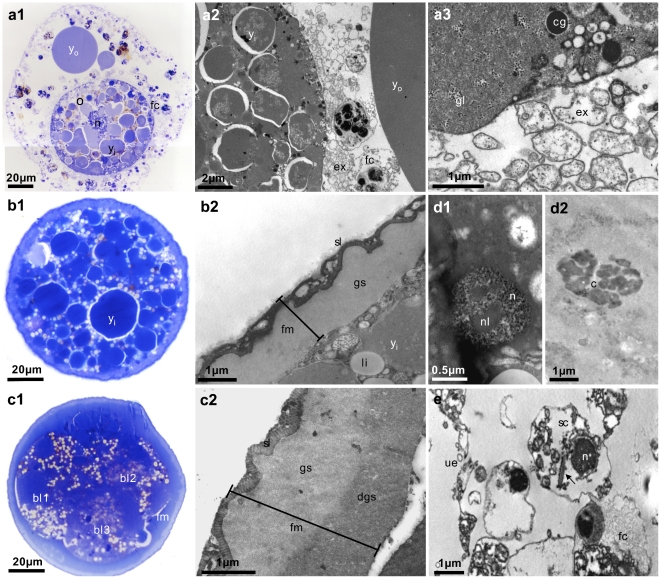
Figure 3. Ultrastructural analyzes of developing Placozoa sp. H2 oocytes and embryos.
Shown are toluidine stained semi-thin sections (left panels) and TEM images (middle and right panels) of maturing oocytes (a) and embryos in different stages (b, c, d). Yolk material inside and outside maturing oocytes and embryos is clearly visible in dark blue in toluidine stained sections (a1, b1, c1) and as moderately electron dense material in TEM images (a2, b2). The early ‘fertilization membrane’ is made up of two layers (b1, b2), whereas three layers are distinguishable in later stages (c1, c2). Additional features not reported before are glycogen granules (a3) and lipid droplets in the oocyte (b1, b2, c1). In some sections nuclei (d1) and chromosomes (d2) were found in blastomers, indicating a normal cell cycle. We identified a putative sperm cell (e) with a retracted flagellum (arrow in e). o = oocyte, yo = yolk outside oocyte, yi = yolk inside oocyte, fc = fiber cell, ex = fiber cell extensions, cg = cortex granulum, gl = glycogen, li = lipid droplet, fm = fertilization membrane, sl = striped layer, gs = ground substance, dgs = dense ground substance, bl = blastomer, n = nucleus, nl = nucleolus, c = metaphase chromosomes, sc = putative sperm cell, ue = upper epithelium.