Figure 9.
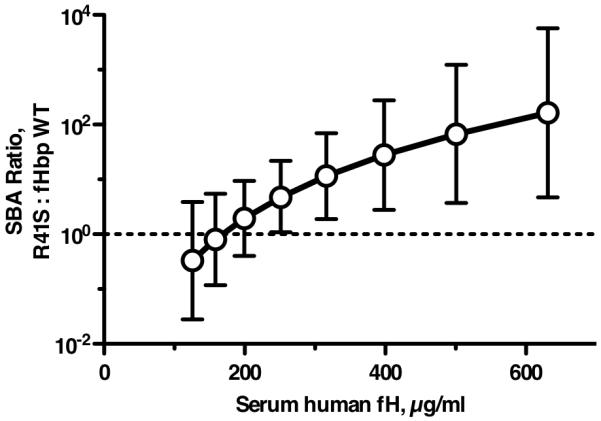
Effect of serum human fH concentrations on ratio of bactericidal antibody responses elicited by R41S mutant fHbp vaccine versus wild-type fHbp vaccine. The respective GMT ratios (R41S mutant : fHbp wild-type) were estimated from the general linear regression model (see text), which showed that the effect of fHbp vaccine type differed by serum fH concentration on bactericidal titer (P=0.018). Based on the regression model, the ratios of the geometric mean bactericidal responses of the group immunized with R41S fHbp vaccine over that of the group immunized with wild-type fHbp vaccine were significantly greater than 1 (in favor of the mutant fHbp vaccine) for all human fH concentrations >250 μg/ml (P<0.05), and for >316 μg/ml (P<0.01).
