Figure 7. Alcohol-induced BBB damage enhances immune cells adhesion.
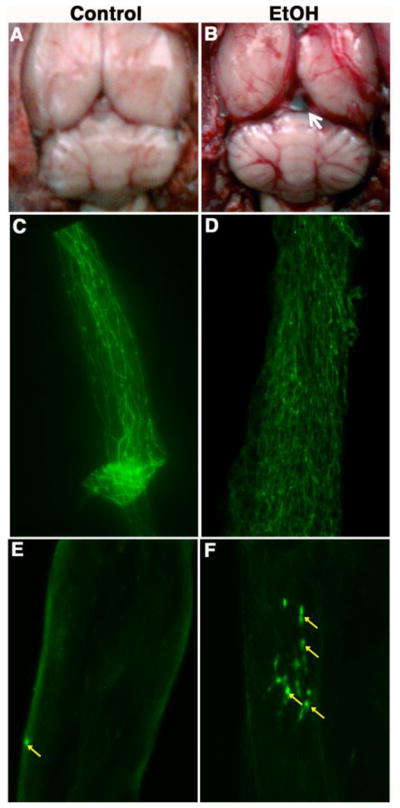
(A) Whole brain structure of control animal. (B) Whole brain structure of ethanol intake animal indicating the breakage of brain microvessels and hemorrhage. The arrow shows the formation of thrombus. (C–D) Immunohistochemical staining of the tight junction protein occludin in an intact brain microvessels of chronic alcohol ingestion compared with pair-fed control. (E–F) Infusion of fluo-3 labeled macrophage into the CCA via implanted catheter. The arrows indicate the aggregations of macrophages at the BBB damage site.
