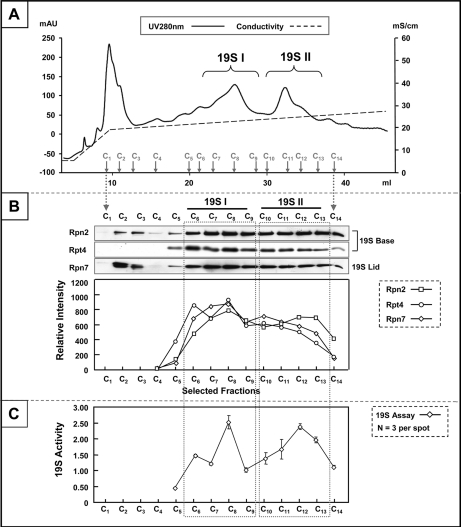
Fig. 1.
Purification of distinct 19S subpopulations from the murine heart. Panel. A, MonoQ chromatography was applied as the final step of murine 19S complex purification. With a slow ramping of salt concentration (shown in the form of conductivity: mS/cm), two distinct subpopulations of 19S complexes (19S I and 19S II) were collected (UV280: mAU). B, The structural integrity of 19S complexes was probed with a panel of antibodies targeting subunits from the “base” (Rpn2, Rpt4) and the “lid” (Rpn7) substructures. Both 19S species were shown to be structurally intact. Densitometry measurement showed a consistent enrichment pattern for 19S subunits in support of the UV280 nm absorption traces (A). C, The biological function of murine cardiac 19S complexes was evaluated as their ability to stimulate 20S proteasome-dependent proteolysis. With ATP as a necessary cofactor, the activity of 19S complexes in selected fractions (C5-C14) was assayed. The relative activities among these fractions were in agreement with both the UV280 nm profile (A) and densitometry trace (B). All analyses were made with equal volume from each chromatographic fraction.