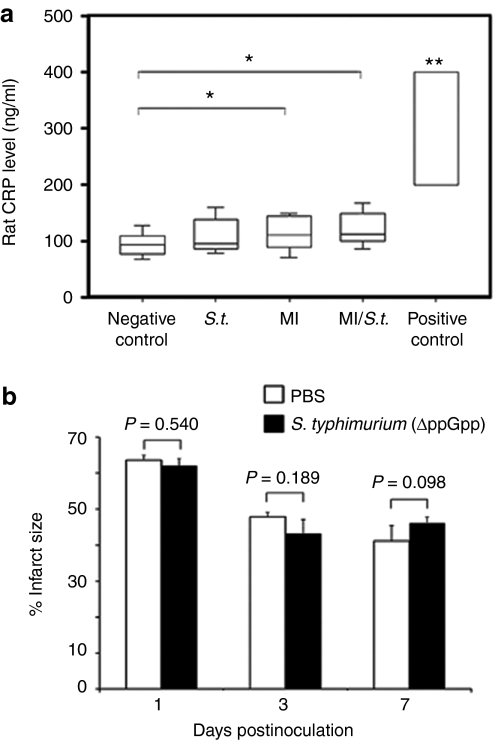
Figure 7.
Systemic and local toxicity associated with ΔppGpp S. typhimurium injection in rats. (a) The levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) after intravenous injection of ΔppGpp S. typhimurium. Plasma CRP levels in sham operated and MI rats (n = 3 each) before and after the injection of Salmonellae (2 × 108 CFUs) were measured at 1 and 5 days post inoculation (dpi). The results are expressed as averages of CRP levels at 1 and 5 dpi. Rats (n = 3) were intravenous injected with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 5 mg/kg for 3 minutes) as a positive control, and blood was drawn 4 hours after injection. Negative control indicates sham operated rats; S.t., sham operated rats with bacterial injection; MI, MI rats without bacterial injection; MI/S.t., MI rats with bacterial injection; positive control, LPS injected rats. Boxes represent the quartiles and whiskers mark the 10th and 90th percentiles. *P = 0.035; **P < 0.01. (b) Change of infarct size associated with ΔppGpp S. typhimurium injection in MI rats. Sprague–Dawley rats (n = 30) with MI were intravenously injected with PBS or ΔppGpp S. typhimurium (2 × 108 CFUs). At 1, 3, or 7 dpi (n = 5 for each group), rats were sacrificed and hearts were excised for triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining. The infarct size was measured using image processing software. MI, myocardial infarction; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.