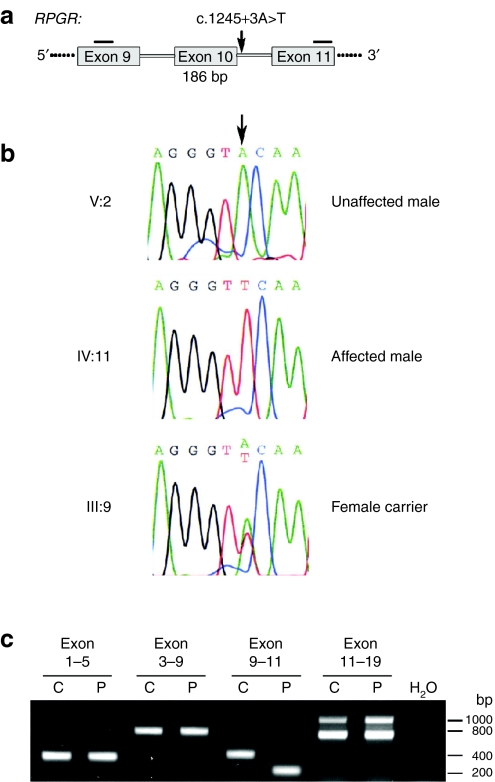
Figure 2.
DNA and RNA analyses of RPGR mutation c.1245+3A>T. (a) Parts of the gene structure of RPGR are shown in a schematic drawing. The position of the mutation is indicated by an arrow. Horizontal bars represent reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) primers. Skipping of RPGR exon 10 during splicing leads to a 186 base pair deletion in the transcript. (b) Sequencing electropherograms of family members V:2, IV:11, III:9. The arrow indicates the nucleotide position which is mutated. Sequencing profiles are shown for the splice donor site of RPGR exon 10: the first three nucleotides are of exonic origin, whereas the last six nucleotides are part of intron 10. (c) RT-PCR products of RPGR exons 1–19. RNA from control (C) or patient (P) fibroblasts were analyzed for splice alterations. The only difference in splicing was detected by amplification of exons 9–11. Sequencing confirmed that exon 10 skipping occurred in the RPGR transcript of the patient cell line. RPGR, retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator gene.