Figure 2. Glycine activates strychnine-sensitive GlyRs in SCN neurons.
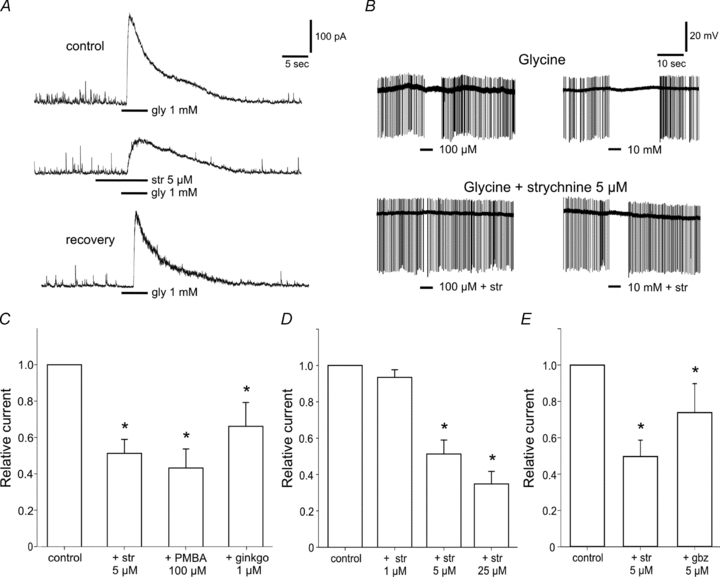
A, typical response to glycine (1 mm) at a holding potential of 0 mV showing an outward current (upper trace) which is reduced by co-application of strychnine (str, 5 μm) (middle trace). The lower trace shows the recovery of the response after wash-out. n = 12. B, extracellular recordings from a SCN neuron in an acute slice. Strychnine (5 μm) reduces the inhibitory effect of glycine on the spike rate (n = 3). C, the GlyR antagonists strychnine (5 μm), PMBA (100 μm) and ginkgolide B (ginkgo, 1 μm) reduce glycine-induced currents by 51, 56 and 34%, respectively (n = 6–12). D, the suppression of the amplitude of the current is enhanced by increasing concentrations of strychnine (1 to 25 μm, n = 8). E, application of gabazine (gbz, 5 μm) together with glycine (1 mm) reduced the current induced by glycine alone to a lesser extent than strychnine (5 μm) (n = 8). *P < 0.05.
