Figure 4. Glycine induced changes in the firing rate of SCN neurons in organotypic cultures.
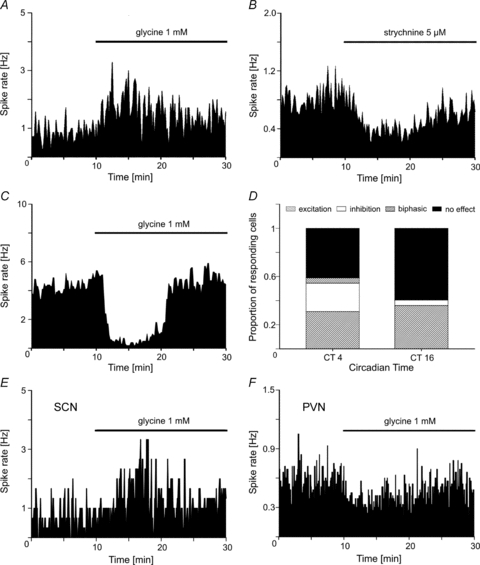
Application of glycine (1 mm) during MEA recordings induces either A, an increase or C, a decrease of the firing rate. The concentrations of the drugs refer to the beginning of the application with the autosampler which is completed after 150 s; then the drug concentration slowly decreases because it is washed out by the superfusion flow. B, in cells that were excited by glycine application, strychnine induces a decrease of the firing rate. D, the proportion of SCN cells responding to glycine with a decrease of their firing rate is more prominent at CT 4 (24%) than at CT 16 (6%). At this time a small subset of SCN neurons (5%) respond to glycine with a biphasic change of their firing rate. n = 58 (CT 4), n = 89 (CT 16). E and F illustrate one experiment where the effects of glycine on the firing rate is opposite in the SCN (E) and in the PVN (F). The bars above the recording traces represent the presence of glycine in the recording chamber.
