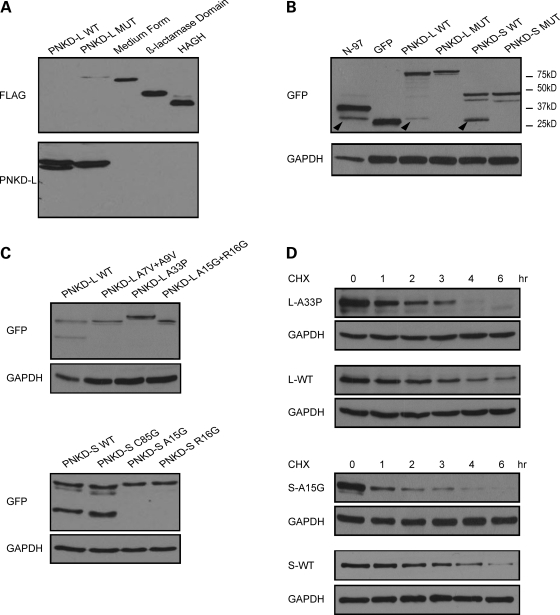
Figure 3.
WT PNKD-L is cleaved at its N-terminus, while mutant PNKD-L is resistant to cleavage. (A) A FLAG epitope was added to the N-terminus of PNKD-L WT or MUT, PNKD-M, PNKD β-lactamase domain, and HAGH. Cell lysates were blotted with FLAG or PNKD-L antibody. (B) GFP was fused to the N-terminus of PNKD-L WT or MUT, PNKD-S WT or MUT, and a fragment containing amino acids 1–79 of the PNKD N-terminus (N-79). Cell lysates were blotted with GFP antibody. Cleaved GFP was detected in all constructs that contain WT N-terminal sequences, the arrowheads indicate the cleaved N-terminal GFP fragments which are slightly larger than GFP alone. (C) GFP was fused to the N-terminus of PNKD-L WT, MUT, A33P, A15G/R16G or PNKD-S WT, C85G, A15G and R16G. GFP cleavage was only detected in WT and C85G. (D) The CHX assay in cells expressing PNKD-L A33P and WT, PNKD-S A15G and WT shows that these mutations also lead to faster degradation.