Figure 3.
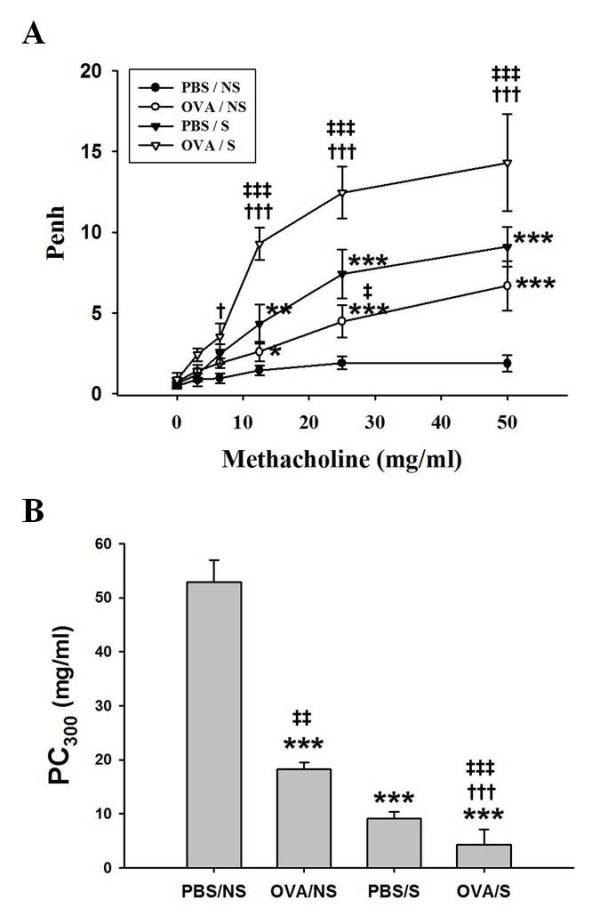
The effects of smoke exposure on airway hyperresponsiveness in OVA-induced asthmatic mice. Experimental conditions and group symbols used were described in Figure 1. Airway hyperresponsiveness was measured at 24 h after last challenge using a whole-body plethysmography as described in "Materials and Methods". Airway responsiveness to aerosolized methacholine (MCh) was measured in conscious, spontaneously breathing mice. Mice were placed into the main chamber and were nebulized first with PBS, then with increasing doses (1.56 to 50 mg/ml) of MCh for 2 min for each nebulization. Readings of breathing parameters were taken for 2 min after each nebulization during which Penh values were determined (A). The PC300 represents the dose of MCh which induces 300% increase in Penh (B). Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. (n = 8). *, P < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 versus PBS/NS mice. †, P < 0.05; †††, P<0.001 versus OVA/NS mice. ‡, P < 0.05; ‡‡, P < 0.01; ‡‡‡, P < 0.001 versus PBS/S mice.
