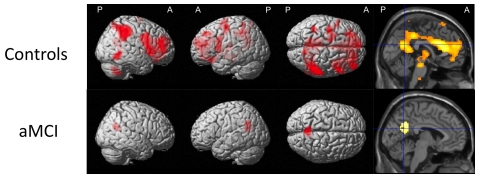
Figure 2. Within-group effect of personal familiarity irrespective of stimulus type.
The figure shows brain areas with relative increase in neural activity for both subject groups when perceiving familiar>unfamiliar stimulus content irrespective of stimulus type. The local maxima are superimposed on a rendered standard single subject brain provided by SPM5. See Table 3 for exact coordinates. R = right, L = left, A = anterior, P = posterior.