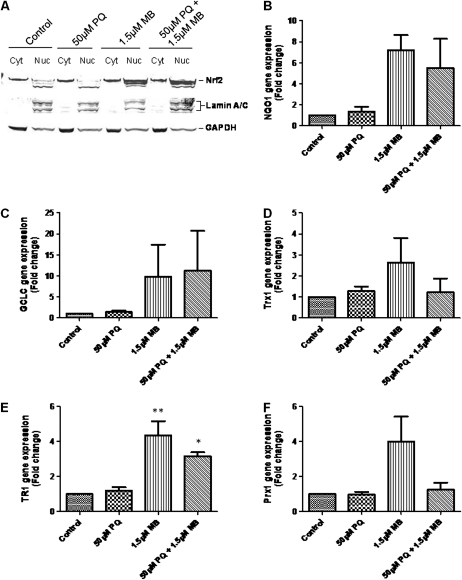
FIG. 6.
MB treatment causes a potent activation of Nrf2. Nuclear translocation of Nrf2 (A) was assessed, and cells were assayed for abundance of Nrf2-responsive genes: (B) γ-glutamylcysteine ligase—catalytic subunit (GCLC), (C) NADPH:quinone oxidoreductase-1 (NQO1), (D) thioredoxin 1 (Trx1), (E) thioredoxin reductase 1 (TR1), and (F) peroxiredoxin 1 (Prx1). Assays were performed in triplicate in at least three independent experiments. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, and data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s post hoc test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).