Fig. 1.
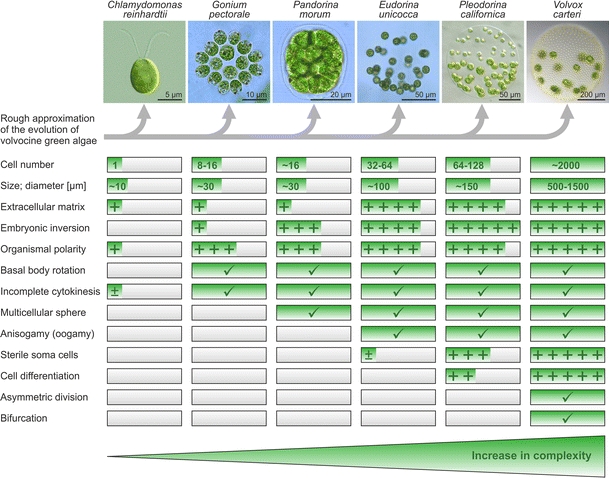
Rough approximation of the evolution of volvocine green algae from unicellular forms to colonial and multicellular forms with increasing complexity. Six representative species with characteristic developmental traits were arranged such that there is a progressive increase from left to right in morphologic and developmental complexity (Kirk 1998, 2000; Prochnik et al. 2010). Check marks indicate that a given trait is present in the respective species. Graded differences in a given trait are indicated by 1–5 plus signs and ± indicates ambiguity or occasional occurrence. The photomicrographs show Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (SAG 11-32b), Gonium pectorale (SAG 12.85), Pandorina morum (SAG 60-1d), Eudorina unicocca (SAG 24-1c), Pleodorina californica (SAG 32.94), and Volvox carteri (Eve). The exact phylogenetic position of these six species is indicated with filled black circles in the evolutionary tree in Fig. 3
