Figure 5. Characteristics of functional classes of distension-sensitive rectal afferents in wild-type and ls/ls mice.
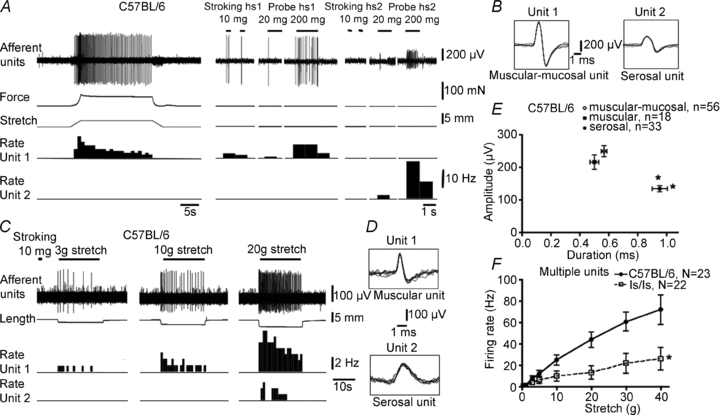
A, wild-type mouse: unit 1 is a muscular-mucosal afferent (sensitive to stroking and probing with light von Frey hairs); unit 2 is a serosal afferent (only activated by 200–500 mg von Frey hair probing. B, superimposed action potentials (×7) of units 1 and 2 confirm single unit recordings. C, recording from a different nerve reveals a muscular afferent (activated by small distensions) and a serosal afferent, with a typically higher distension threshold. D, superimposed action potentials confirm single unit recordings and show characteristic shapes of action potentials. E, plot of action potential amplitude and half-duration for each class (muscular, muscular-mucosal and serosal) show consistent differences in profiles. Typically, serosal afferents had a characteristic smaller amplitude and longer duration than muscular-mucosal afferents. F, comparison of total stretch-evoked firing from all functional classes of afferents (multi-unit recording from rectal nerves) for control C57BL/6 and ls/ls mice. Total stretch sensitivity of afferents was significantly reduced in ls/ls mice compared with controls.
