Figure 11. A numerical simulation of the effects of noise on calculation of baroreflex transfer functions.
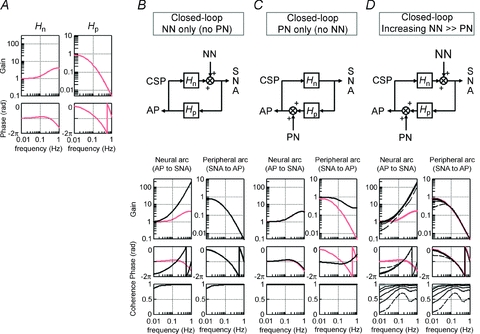
Noise (Gaussian white-noise) is introduced to the neural and/or peripheral arcs in closed-loop-spontaneous baroreflex condition, where CSP equals AP (see Figure 1C). A, the original baroreflex transfer functions of the neural (Hn, left panel) and peripheral (Hp, right panel) arcs. Hn is modelled using derivative and high-cut filter characteristics with a pure delay, and Hp using the second-order low-pass filter with a pure delay (see Appendix B). Units of gain are a.u. mmHg−1 for Hn and mmHg a.u.−1 for Hp, respectively. B–D, block diagrams (upper panels) and closed-loop-spontaneous transfer functions (lower panels); calculated from AP to SNA as the neural arc (left lower panel) and from SNA to AP as the peripheral arc (right lower panel). The open-loop transfer functions (Hn, Hp) are included as reference (gray lines). Units of gain are a.u. mmHg−1 for the neural arc and mmHg a.u.−1 for the peripheral arc, respectively. B, first simulation: noise (0.029, 0.117, 0.264, 0.732 and 2.928 × 103 au2) is present only in the neural arc. The same results are obtained irrespective of the noise intensity. The closed-loop-spontaneous transfer function of the neural arc is totally different from the open-loop transfer function Hn, whereas that of the peripheral arc overlaps with Hp. C: Second simulation: noise (0.029, 0.117, 0.264, 0.732 and 2.928 × 103 mmHg2 is present only in the peripheral arc. The same results are obtained irrespective of the noise intensity. The closed-loop-spontaneous transfer function of the neural arc overlaps the open-loop transfer function Hn, whereas that of the peripheral arc is markedly different from Hn. D, third simulation: noise with incremental intensity [from 0.029 (broken line) to 0.117, 0.264, 0.732 and 2.928 (solid lines) × 103 au2] is present in the neural arc, while a small constant noise (29 mmHg2) is present in the peripheral arc. The closed-loop-spontaneous transfer function of the neural arc is different from the open-loop transfer function of Hn, whereas that of the peripheral arc approaches Hp and the two become overlapped as the noise in the neural arc increases. Hn, neural arc transfer function; Hp, peripheral arc transfer function, NN, unknown neural noise; PN, unknown peripheral noise.
